Clean • Professional
Spring Boot annotations are metadata markers that instruct the Spring container on configuration, bean management, and runtime behavior. They eliminate complex XML configurations, simplify dependency injection, and make creating REST APIs faster and more maintainable.
These annotations are used to bootstrap a Spring Boot application and initialize the Spring container.
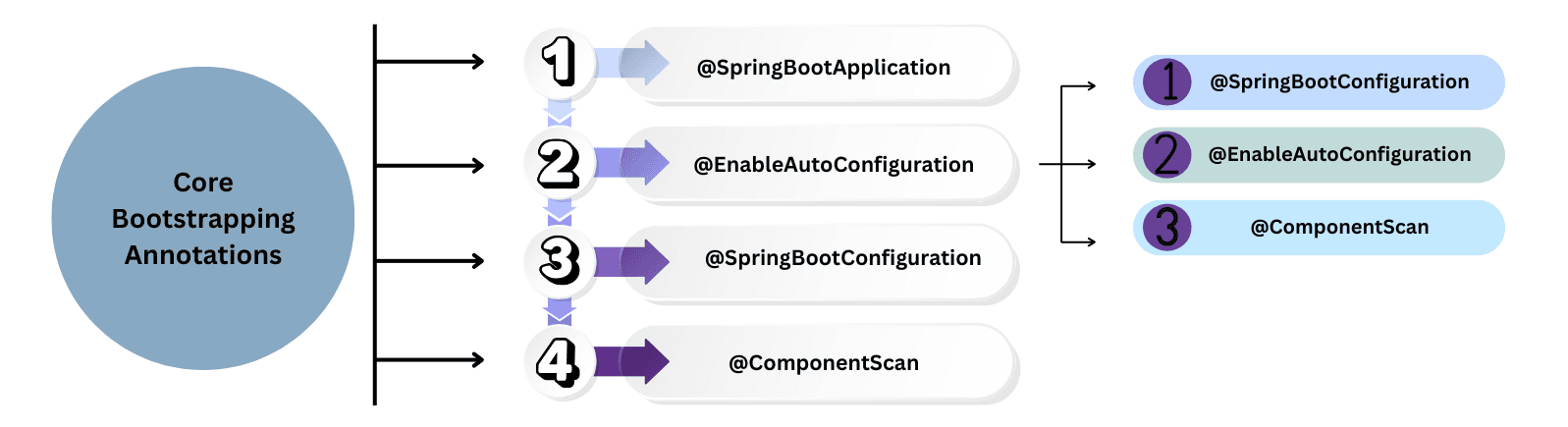
@SpringBootApplication
Marks the main entry point of a Spring Boot application.
Internally includes three annotations:
@SpringBootConfiguration → Marks a class as a configuration source.@EnableAutoConfiguration → Automatically configures beans based on classpath dependencies.@ComponentScan → Scans packages for Spring components (@Component, @Service, @Repository).Example:
@SpringBootApplication
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MyApplication.class, args);
}
}
@EnableAutoConfiguration
spring-boot-starter-web is on the classpath, it auto-configures DispatcherServlet, embedded Tomcat, and MVC beans.@SpringBootConfiguration
@Configuration.@SpringBootApplication.@ComponentScan
@Component, @Service, @Repository, and @Controller.@SpringBootApplication and its sub-packages.@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.example.services")
public class AppConfig { }
Spring Boot uses Dependency Injection (DI) to manage objects (beans) automatically. This makes your code loosely coupled, easier to test, and maintainable. To work with DI, Spring provides several key annotations for defining and managing beans.
@Component
Example:
@Component
public class NotificationService {
public void send(String message) {
System.out.println("Sending: " + message);
}
}
@Service
@Component.Example:
@Service
public class UserService {
public void createUser(String name) {
System.out.println("Creating user: " + name);
}
}
@Repository
@Component.DataAccessException.Example:
@Repository
public class UserRepository {
public void save(User user) {
System.out.println("User saved: " + user.getName());
}
}
@Controller
Example:
@Controller
public class HomeController {
@GetMapping("/")
public String home() {
return "home"; // returns view name
}
}
@RestController
@Controller + @ResponseBody.Example:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/users")
public class UserRestController {
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public User getUser(@PathVariable int id) {
return new User(id, "John Doe");
}
}
@Autowired
Example (field injection):
@Service
public class OrderService {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
public void placeOrder(String userName) {
System.out.println("Placing order for: " + userName);
}
}
Example (constructor injection - recommended):
@Service
public class OrderService {
private final UserRepository userRepository;
@Autowired
public OrderService(UserRepository userRepository) {
this.userRepository = userRepository;
}
}
@Qualifier
@Autowired when multiple beans of the same type exist.@Service
public class PaymentService {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("paypalPayment")
private PaymentProcessor paymentProcessor;
}
@Primary
@Primary bean should exist per type.@Component
@Primary
public class CreditCardPayment implements PaymentProcessor { }
Spring Boot provides annotations to define configuration classes, beans, and inject properties from files like application.properties or application.yml. These annotations make your application flexible, maintainable, and environment-friendly.
@Configuration
@Configuration can define beans using @Bean.Example:
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public MyService myService() {
return new MyServiceImpl();
}
}
@Bean
@Configuration classes.Example:
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public UserService userService() {
return new UserServiceImpl();
}
}
@Value
application.properties or application.yml.Example:
@Component
public class AppInfo {
@Value("${app.name}")
private String appName;
@Value("${app.version:1.0}")
private String appVersion; // default 1.0
}
@ConfigurationProperties
application.properties or application.yml to a Java POJO.@Component) or registered via @EnableConfigurationProperties.Example (application.yml):
app:
name: MyApp
version: 2.0
features:
login: true
signup: false
Example (Java class):
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "app")
public class AppProperties {
private String name;
private double version;
private Features features;
// getters and setters
public static class Features {
private boolean login;
private boolean signup;
// getters and setters
}
}
@PropertySource
application.properties.Example:
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:custom.properties")
public class CustomConfig { }
Spring Boot makes it easy to build web applications and REST APIs. These annotations are mainly used in controllers to handle HTTP requests and responses.
@Controller
Example:
@Controller
public class HomeController {
@GetMapping("/")
public String home() {
return "home"; // returns view name
}
}
@RestController
@Controller + @ResponseBody.Example:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/users")
public class UserRestController {
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public User getUser(@PathVariable int id) {
return new User(id, "John Doe");
}
}
@RequestMapping
Example:
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/products")
public class ProductController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/list", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String listProducts() {
return "productList";
}
}
Shorthand Request Mappings
Spring Boot provides specific annotations for common HTTP methods:
| Annotation | HTTP Method |
|---|---|
@GetMapping | GET |
@PostMapping | POST |
@PutMapping | PUT |
@DeleteMapping | DELETE |
@PatchMapping | PATCH |
Example:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/orders")
public class OrderController {
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Order getOrder(@PathVariable int id) { ... }
@PostMapping
public Order createOrder(@RequestBody Order order) { ... }
}
@PathVariable
@GetMapping("/users/{id}")
public User getUser(@PathVariable int id) {
return userService.getUserById(id);
}
@RequestParam
@GetMapping("/search")
public List<User> searchUsers(@RequestParam String name) {
return userService.findByName(name);
}
@RequestBody
@PostMapping("/users")
public User createUser(@RequestBody User user) {
return userService.saveUser(user);
}
@ResponseBody
@RestController since it’s included by default.@CrossOrigin
@CrossOrigin(origins = "<http://localhost:3000>")
@GetMapping("/users")
public List<User> getUsers() {
return userService.getAllUsers();
}
Spring Boot allows you to load beans or configurations conditionally, depending on properties, environment, or active profiles. This makes your application flexible, environment-aware, and production-ready.
@ConditionalOnProperty
application.properties or application.yml.Example:
@Component
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "feature.payment.enabled", havingValue = "true")
public class PaymentService {
public void processPayment() {
System.out.println("Processing payment...");
}
}
application.properties:
feature.payment.enabled=true
false or missing, Spring will not create the bean.@Profile
Example:
@Component
@Profile("dev")
public class DevDatabaseConfig implements DatabaseConfig {
// Development database settings
}
@Component
@Profile("prod")
public class ProdDatabaseConfig implements DatabaseConfig {
// Production database settings
}
Activating a profile:
In application.properties:
spring.profiles.active=dev
Or via command line:
java -jar myapp.jar --spring.profiles.active=prod
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
Example:
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public UserService userService() {
return new DefaultUserService();
}
@ConditionalOnBean
Example:
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(UserRepository.class)
public UserService userService(UserRepository repo) {
return new UserServiceImpl(repo);
}
@ConditionalOnClass
Example:
@ConditionalOnClass(name = "com.external.PaymentGateway")
@Bean
public PaymentService paymentService() {
return new PaymentServiceImpl();
}
Spring Boot allows you to run tasks at scheduled intervals or execute methods asynchronously in separate threads. These features are essential for background jobs, batch processing, and performance optimization.
@EnableScheduling
Example:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableScheduling
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MyApplication.class, args);
}
}
@Scheduled
Example (fixed rate):
@Component
public class ReportScheduler {
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 5000) // runs every 5 seconds
public void generateReport() {
System.out.println("Generating report at " + LocalDateTime.now());
}
}
Example (cron expression):
@Scheduled(cron = "0 0 9 * * ?") // runs every day at 9 AM
public void dailyReport() {
System.out.println("Daily report generated");
}
Notes:
fixedRate → interval between method start times.fixedDelay → interval between method completion and next start.cron → flexible scheduling using cron expressions.@EnableAsync
@Async.Example:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAsync
public class MyApplication { ... }
@Async
Example:
@Service
public class EmailService {
@Async
public void sendEmail(String recipient) {
System.out.println("Sending email to " + recipient + " in thread " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
Notes:
@EnableAsync and Executor beans.Spring Boot provides several additional annotations that are useful for transactions, event handling, bean management, and configuration organization.
@Transactional
Example:
@Service
public class UserService {
@Transactional
public void createUserAndProfile(User user, Profile profile) {
userRepository.save(user);
profileRepository.save(profile);
// Both succeed or both rollback on error
}
}
@ComponentScan
@Component, @Service, @Repository, and @Controller.Example:
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.example.services")
public class AppConfig { }
@Import
Example:
@Configuration
@Import(DatabaseConfig.class)
public class AppConfig { }
@EventListener
Example:
@Component
public class UserEventListener {
@EventListener
public void handleUserCreated(UserCreatedEvent event) {
System.out.println("User created: " + event.getUserName());
}
}
| Category | Annotations | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Core Bootstrapping | @SpringBootApplication, @EnableAutoConfiguration, @SpringBootConfiguration, @ComponentScan | Initialize Spring Boot app and configure beans automatically |
| Conditional & Profiles | @ConditionalOnClass, @ConditionalOnMissingBean, @ConditionalOnProperty, @Profile | Register beans conditionally based on classpath, properties, or active profiles |
| Web & REST | @Controller, @RestController, @RequestMapping, @GetMapping, @RequestParam, @PathVariable, @RequestBody, @CrossOrigin | Map HTTP requests, handle REST APIs, and enable CORS |
| Dependency Injection & Bean Management | @Component, @Service, @Repository, @Autowired, @Bean, @Value, @Qualifier, @Primary | Define, inject, and manage beans automatically |
| Scheduling & Async | @EnableScheduling, @Scheduled, @EnableAsync, @Async | Execute tasks periodically or asynchronously |
| Transaction & Configuration | @Transactional, @ConfigurationProperties, @PropertySource | Manage transactions and bind configuration properties |
Always use @SpringBootApplication as the main entry point.
@Service, @Repository, @Controller).