Clean • Professional
Spring Boot’s Auto-Configuration Architecture is the internal system that automatically configures your application based on the dependencies, classpath, environment, and missing beans.
It eliminates boilerplate setup and makes Spring Boot applications run with minimal configuration.
Auto-Configuration means:
Example:
Add spring-boot-starter-web → Boot automatically configures:
There are 5 main internal components:
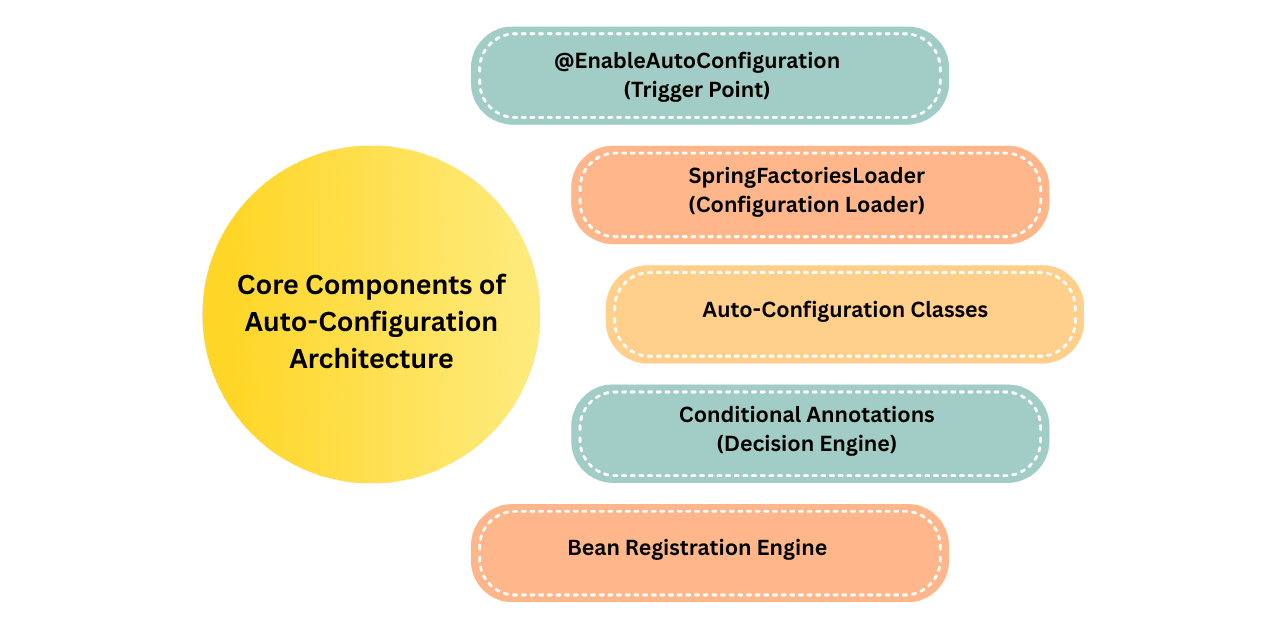
@EnableAutoConfiguration (Trigger Point)This annotation triggers Spring Boot’s auto-configuration.
It does two things:
It is included inside @SpringBootApplication.
Spring Boot uses SpringFactoriesLoader to scan:
META-INF/spring.factories
This file contains a list of all available auto-configurations.
Example snippet:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration
This is like a registry of all auto-configuration classes Boot can use.
These classes are located in:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.*
Each class configures a particular feature:
Each is activated only when required.
Auto-Configuration uses conditional annotations to decide:
Common annotations:
@ConditionalOnClass@ConditionalOnMissingBean@ConditionalOnProperty@ConditionalOnWebApplication@ConditionalOnResourceThese make auto-configuration smart and context-aware.
Example:
@ConditionalOnClass(DataSource.class)
public class DataSourceAutoConfiguration { }
Only configures DataSource if DataSource.class exists.
Once conditions pass:
@ConditionalOnMissingBeanExample:
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public ObjectMapper objectMapper() {
return new ObjectMapper();
}
If you provide your own ObjectMapper, Boot won’t create another.
Here is the internal flow:
@EnableAutoConfigurationspring.factoriesYou add:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
Boot detects:
So it auto-configures:
Example:
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class)
Spring Boot’s Auto-Configuration Architecture is a smart engine that detects dependencies and automatically configures only what your application needs using conditional logic.