Clean • Professional
Spring MVC Architecture is a request-driven web framework that follows the Model-View-Controller (MVC) design pattern. It is part of the Spring Framework and is widely used to build robust, scalable, and maintainable web applications.
The main goal of Spring MVC is to separate concerns by dividing an application into three interconnected components:
@Controller, @RestController, @RequestMapping, etc.Learn about the key building blocks of Spring MVC Architecture, including DispatcherServlet, Controllers, Models, Views, and HttpMessageConverters, that power request handling and response rendering in modern web applications.
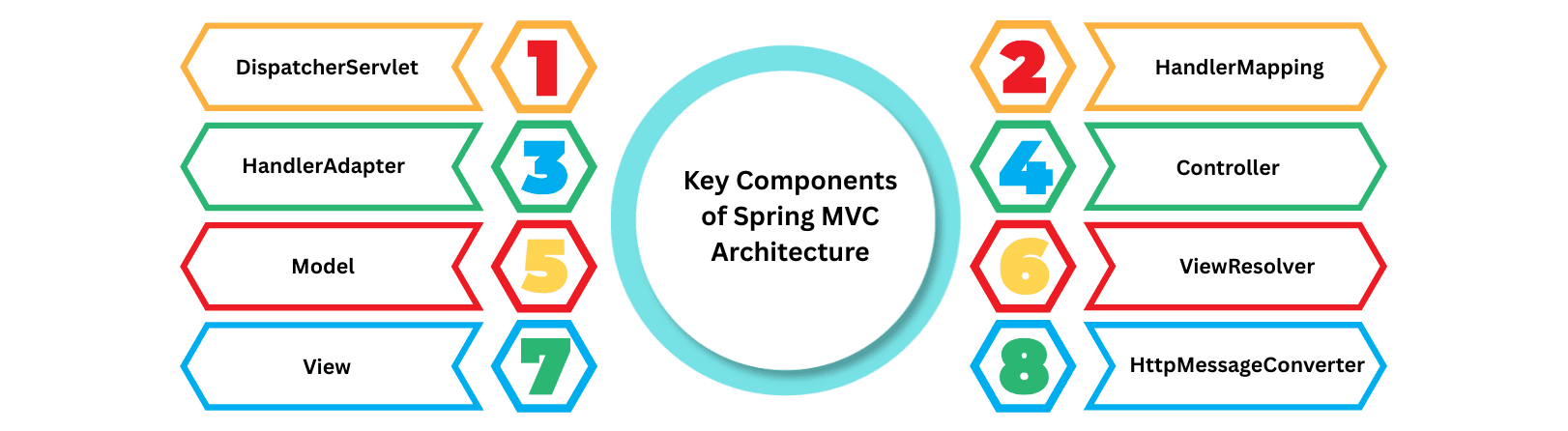
The DispatcherServlet is the front controller in Spring MVC. It intercepts all incoming HTTP requests and manages the entire request-processing lifecycle. This includes routing requests to the appropriate controllers, invoking handler methods, and rendering responses. In Spring Boot, it is auto-configured, while in traditional Spring MVC, it can be configured in web.xml.
The HandlerMapping maps incoming request URLs to the appropriate controller methods. It uses annotations like @RequestMapping, @GetMapping, and @PostMapping to identify which controller method should handle the request.
Example:
@GetMapping("/users/{id}")
public User getUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
return userService.getUserById(id);
}
The HandlerAdapter acts as a bridge between the DispatcherServlet and the controller method. It prepares the method arguments (e.g., @RequestParam, @PathVariable, @ModelAttribute) and invokes the controller. Spring automatically provides adapters like RequestMappingHandlerAdapter for annotated controllers.
Controllers contain the application logic. They process user input, interact with the service layer, and return either a ModelAndView object for UI views or a response object for REST APIs.
Example (UI View):
@Controller
public class UserController {
@GetMapping("/users/{id}")
public ModelAndView userDetail(@PathVariable Long id) {
User user = userService.getUserById(id);
ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView("userView");
mv.addObject("user", user);
return mv;
}
}
Example (REST API):
@RestController
public class UserRestController {
@GetMapping("/users/{id}")
public User getUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
return userService.getUserById(id);
}
}
The Model holds the application data that needs to be displayed in the view or returned in the response. It typically consists of Java objects, DTOs, or entities that carry data between the controller and view.
Example:
mv.addObject("user", user); // Adding user data to the model
The ViewResolver resolves logical view names returned by the controller to actual templates. This allows controllers to remain decoupled from view technologies.
Example:
Logical view name "userView" → JSP file /WEB-INF/views/userView.jsp.
The View is responsible for rendering the final output. It can generate HTML pages for UI or use HttpMessageConverters to produce JSON/XML for REST APIs.
Example (Thymeleaf/JSP):
<p>User Name: ${user.name}</p>
Example (REST JSON):
{
"id": 1,
"name": "John Doe"
}
The HttpMessageConverter automatically converts Java objects returned by controllers into JSON, XML, or other formats based on the client’s Accept header. It also converts incoming requests into Java objects for method parameters.
Example (REST API):
@RestController
public class UserRestController {
@GetMapping("/users/{id}")
public User getUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
return userService.getUserById(id);
}
}
Spring automatically converts the User object into JSON:
{
"id": 1,
"name": "John Doe"
}
GET /users/1.The DispatcherServlet in Spring MVC is the front controller that manages the entire request lifecycle. It coordinates request handling, controller execution, business logic, and response rendering. Below is a detailed step-by-step flow of how a request is processed.
A client (browser, mobile app, Postman) sends a request to the server.
Example:
GET /users/1
web.xml in traditional Spring or auto-configured in Spring Boot.DispatcherServlet asks HandlerMapping to find the correct controller method for the URL and HTTP method.
Example Controller:
@GetMapping("/users/{id}")
public User getUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
return userService.getUserById(id);
}
@RequestParam, @PathVariable, @ModelAttribute).Example: Fetch user by ID
User user = userRepository.findById(id).orElse(null);
Controller returns ModelAndView for UI rendering or a response object for REST.
REST Example:
return new ResponseEntity<>(user, HttpStatus.OK);
userView → userView.jsp).Example JSON Response:
{
"id": 1,
"name": "John Doe"
}
Client Request (HTTP)
│
▼
DispatcherServlet (Front Controller)
│
▼
HandlerMapping (Find Controller)
│
▼
HandlerAdapter (Invoke Controller)
│
▼
Controller (Processes Request)
│
▼
Service Layer (Business Logic) → Repository Layer (Database)
│
▼
ModelAndView / Response Object
│
▼
ViewResolver (Resolve Template)
│
▼
View / HttpMessageConverter (Render HTML/JSON/XML)
│
▼
Response Sent to Client
| Feature | Spring MVC | Spring Boot Web MVC |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A web framework within Spring for building web applications using the MVC pattern. | A Spring Boot module that builds on Spring MVC, providing auto-configuration and starter dependencies for rapid web app development. |
| Configuration | Requires manual setup of DispatcherServlet, view resolvers, web.xml, and other beans. | Provides automatic configuration, embedded server, and pre-configured defaults for faster development. |
| Setup Complexity | More boilerplate code and XML or Java configuration required. | Minimal setup, often just adding spring-boot-starter-web dependency. |
| Embedded Server | Does not include an embedded server; must configure Tomcat, Jetty, or another server manually. | Comes with embedded Tomcat/Jetty/Undertow, making apps standalone. |
| Starter Dependencies | No starter dependencies; developers manage all dependencies manually. | Provides starter dependencies like spring-boot-starter-web, spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf, etc. |
| Application Type | Suited for traditional web applications, more flexible for custom setups. | Optimized for rapid REST APIs, microservices, and modern web apps. |
| Deployment | Typically packaged as a WAR file and deployed to an external server. | Can be packaged as JAR with embedded server and run independently. |
| Development Speed | Slower due to manual configuration and setup. | Faster, thanks to auto-configuration, embedded server, and starter dependencies. |
| Learning Curve | Higher, as developers must configure most components manually. | Lower, ideal for beginners or rapid prototyping. |
@Controller, @RestController, @RequestMapping, etc.