Clean • Professional
In Spring, bean scope defines the lifecycle and visibility of a bean in the application context. It determines how many instances of a bean are created and how long they live.
Definition
Bean Scope is the lifecycle and visibility of a Spring bean within the Spring container.
Singleton is the default scope in Spring.
@Component
publicclassUserService { }
Only ONE instance of UserService is created for the entire application.
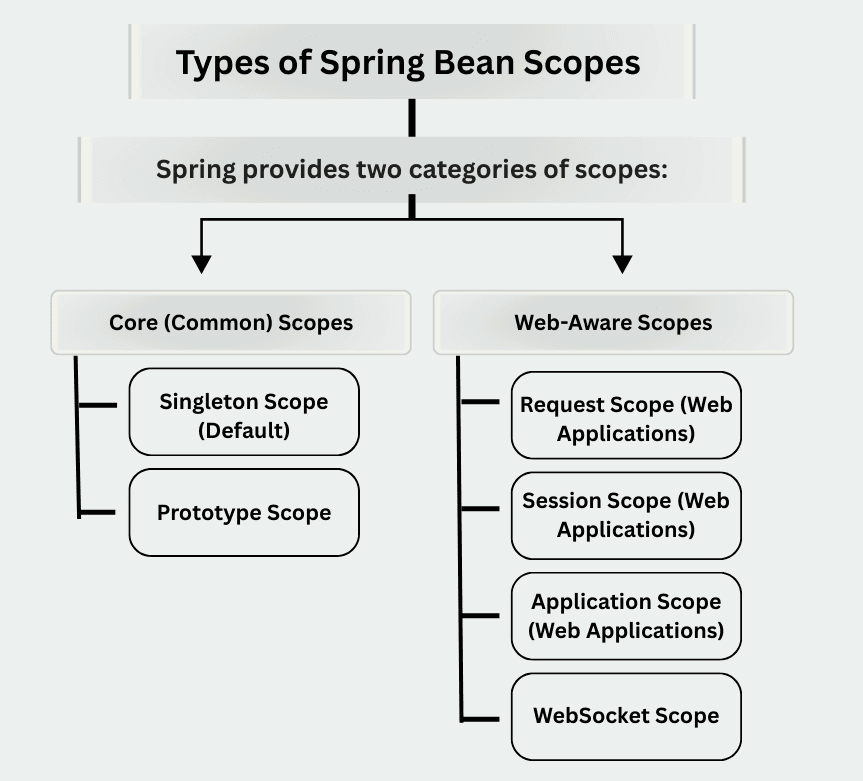
Spring provides two categories of scopes:
Used in all Spring applications
Used in Spring Web / Spring Boot web applications
Only one instance of the bean is created per Spring IoC container.
@Component
@Scope("singleton")// optional, default
publicclassSingletonService { }
Example:
@Autowired
private SingletonService service1;
@Autowired
private SingletonService service2;
// service1 == service2 → true (same instance)
Behavior
ApplicationStart
↓
One Bean Created
↓
Shared Everywhere
Key Points:
A new bean instance is created every time it is requested.
@Component
@Scope("prototype")
publicclassPrototypeService { }
Example:
@Autowired
private PrototypeService p1;
@Autowired
private PrototypeService p2;
// p1 == p2 → false (different instances)
Behavior
Each getBean()call
↓
NewObject Created
Key Points:
@LookupOne bean instance is created per HTTP request.
@Scope("request")@Component
@Scope("request")
publicclassRequestScopedBean { }
Use Case:
Key Points:
One bean instance is created per HTTP session.
@Scope("session")@Component
@Scope("session")
publicclassSessionScopedBean { }
Use Case:
Key Points:
One bean instance is created per ServletContext.
@Scope("application")@Component
@Scope("application")
publicclassAppScopedBean { }
Use Case:
Key Points:
One bean instance is created per WebSocket session.
@Scope("websocket")@Component
@Scope("websocket")
publicclassWebSocketBean { }
Use Case:
Key Points:
Bean scope helps you:
Singleton + State = Danger
Wrong:
@Service
publicclassOrderService {
private Order order;// not thread-safe
}
Correct:
@Service
publicclassOrderService {
publicvoidprocess(Order order) { }
}
| Scope | Example |
|---|---|
| Singleton | Electricity meter |
| Prototype | Disposable cup |
| Request | Restaurant order |
| Session | Shopping cart |
| Application | Mall directory |
| WebSocket | Live chat |
| Scope | Instance Per | Lifecycle | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Singleton | Spring container | Container lifecycle | Stateless services, utilities |
| Prototype | Each injection | Caller manages lifecycle | Stateful, temporary objects |
| Request | HTTP request | Request lifecycle | Request-specific data |
| Session | HTTP session | Session lifecycle | User session-specific data |
| Application | ServletContext | Application lifecycle | Shared caches, global resources |
| WebSocket | WebSocket session | WebSocket session | WebSocket session state |
@Lookup, ObjectFactory, or Provider to avoid stale references.