Clean • Professional
Spring AOP is a framework that modularizes cross-cutting concerns like logging, security, and transactions in Spring applications.
It is based on seven core concepts:
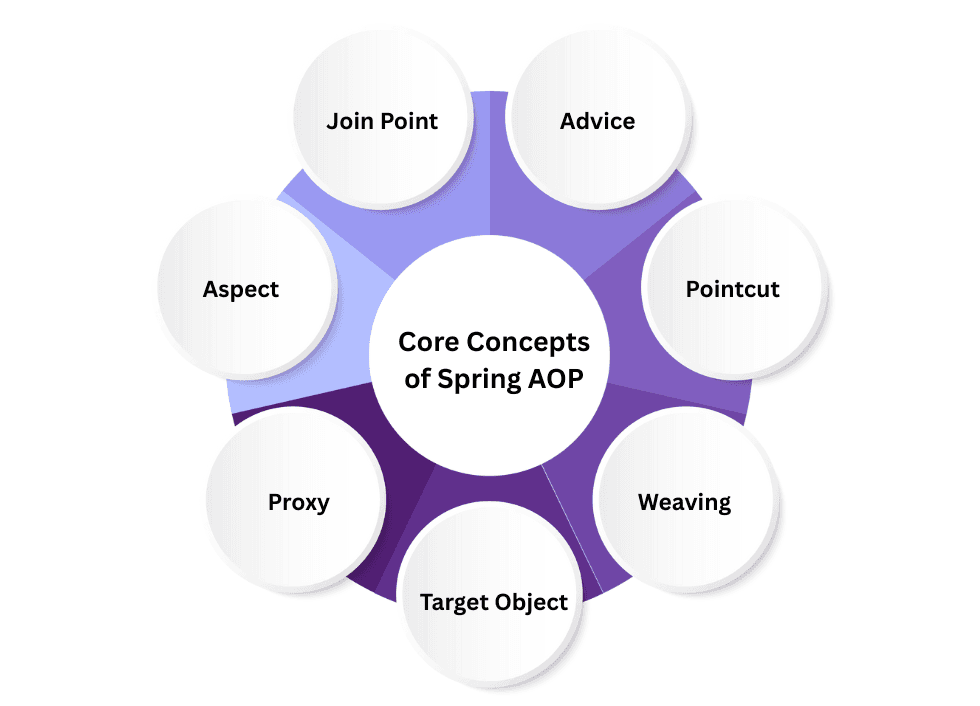
Understanding these concepts helps in building clean, maintainable, and scalable Spring applications without mixing business logic with cross-cutting code.
A module that encapsulates a cross-cutting concern, such as logging, security, or transaction management.
@AspectExample:
@Aspect
@Component
publicclassLoggingAspect {
@Before("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")
publicvoidlogBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("Executing method: " + joinPoint.getSignature());
}
}
LoggingAspect encapsulates all logging-related behavior and can contain multiple advice methods.
A specific point in program execution where an aspect can be applied.
Example:
@Before("execution(* com.example.service.PaymentService.*(..))")
publicvoidlogBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("Method called: " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
}
Here, Each method execution in the service package is a join point.
Advice is the action taken by an aspect at a join point.
Types of Advice: Spring AOP provides different Advice types that define when cross-cutting logic (logging, security, transactions, etc.) executes relative to a method call.
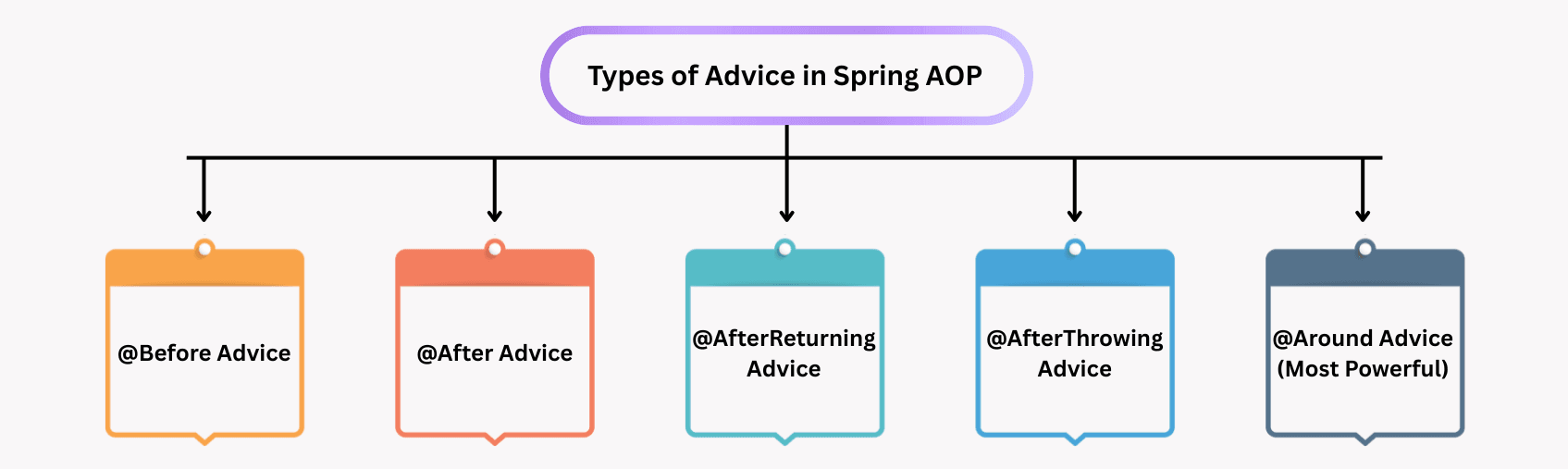
@Before Advice@Before("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")
publicvoidbefore() {
System.out.println("Before method execution");
}
@After Advice@After("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")
publicvoidafter() {
System.out.println("After method execution");
}
@AfterReturning Advice@AfterReturning(pointcut="execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))",
returning="result")
publicvoidafterReturn(Object result) {
System.out.println("Returned: " + result);
}
@AfterThrowing Advice@AfterThrowing(pointcut="execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))",
throwing="ex")
publicvoidafterThrow(Exception ex) {
System.out.println("Exception: " + ex.getMessage());
}
@Around Advice@Around("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")
public Objectaround(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp)throws Throwable {
return pjp.proceed();
}
| Type | When It Executes | Use Case Examples |
|---|---|---|
| @Before | Before method execution | Logging, validation, security |
| @After | After method execution (finally) | Cleanup, auditing |
| @AfterReturning | After successful method return | Logging return values, post-processing |
| @AfterThrowing | After method throws an exception | Exception handling, error logging |
| @Around | Before & after; can modify input/output | Transactions, performance monitoring |
Expression defining which join points an advice should apply to.
Example:
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")
publicvoidserviceMethods() {}
@Before("serviceMethods()")
publicvoidlogBefore() { ... }
✅ All methods in the service package are selected for logging.
&&, ||, !.Process of linking aspects to target objects so that advice runs at join points.
Types of Weaving: Weaving is the process of linking an aspect (cross-cutting logic) with the target object at specific join points.
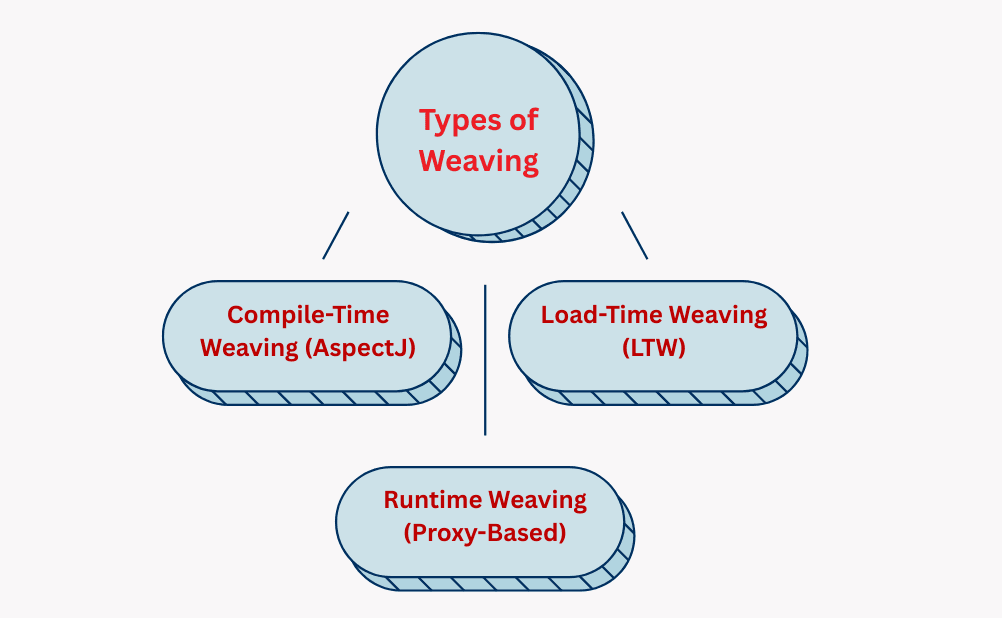
.class files.Example:
Aspect
@Aspect
publicclassLogAspect {
@Before("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")
publicvoidlog() {
System.out.println("Logging before method");
}
}
Example:
Configuration
@EnableLoadTimeWeaving
@Configuration
publicclassAppConfig {}
Aspect
@Aspect
publicclassSecurityAspect {
@Before("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")
publicvoidcheckSecurity() {
System.out.println("Security check");
}
}
Example:
Service
@Service
publicclassOrderService {
publicvoidplaceOrder() {
System.out.println("Order placed");
}
}
Aspect
@Aspect
@Component
publicclassLoggingAspect {
@Before("execution(* com.example.service.OrderService.*(..))")
publicvoidlogBefore() {
System.out.println("Before Order Service");
}
}
Output
BeforeOrderService
Orderplaced
The actual bean/object being advised by an aspect.
Example:
@Service
publicclassPaymentService {
public Stringpay(String user, double amount) { ... }
}
✅ PaymentService is the target object whose methods are intercepted by aspects.
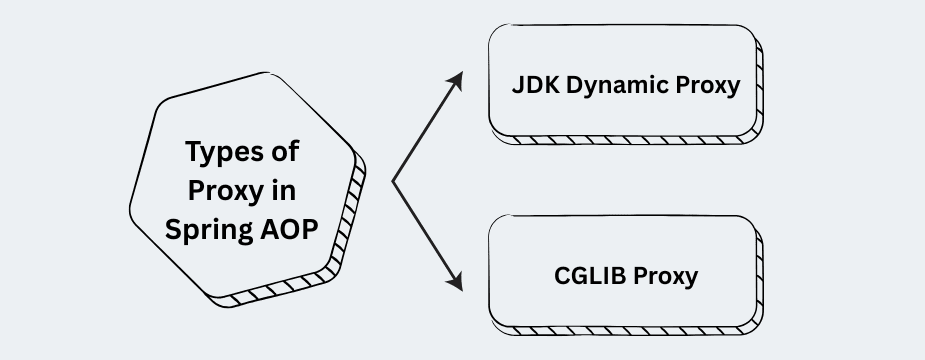
A Spring-generated wrapper around the target object.
Types: Spring AOP uses proxies to implement aspects at runtime. There are two main proxy types:
Example
publicinterfaceOrderService {
voidplaceOrder();
}
@Service
publicclassOrderServiceImplimplementsOrderService {
publicvoidplaceOrder() {
System.out.println("Order placed");
}
}
@Aspect
@Component
publicclassLoggingAspect {
@Before("execution(* com.example.service.OrderService.*(..))")
publicvoidlog() {
System.out.println("Logging before method");
}
}
Output
Loggingbeforemethod
Order placed
Example
@Service
publicclassPaymentService {
publicvoidprocessPayment() {
System.out.println("Payment processed");
}
}
@Aspect
@Component
publicclassLoggingAspect {
@Before("execution(* com.example.service.PaymentService.*(..))")
publicvoidlog() {
System.out.println("Logging before method");
}
}
Output
Loggingbeforemethod
Payment processed
Flow Example:
[ClientCall]
|
v
[ProxyObject]--> Executes @Before Advice
|
v
[TargetObjectMethod Execution]
|
v
[ProxyObject]--> Executes @After / @Around Advice
|
v
[Returnto Client]
| Concept | Definition / Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Aspect | Encapsulates cross-cutting logic (advice + pointcuts) | LoggingAspect |
| JoinPoint | Execution point where advice can run | Method execution |
| Advice | Action performed at a join point | @Before, @AfterReturning |
| Pointcut | Expression specifying which join points to intercept | "execution(* com.service.*.*(..))" |
| Weaving | Linking aspects to target objects | Runtime (Spring proxy) |
| Target Object | Bean being advised | PaymentService |
| Proxy | Wrapper applying advice transparently | Spring-generated proxy |
Spring AOP allows developers to modularize cross-cutting concerns like logging, security, and transactions without cluttering business logic. By using aspects, advice, pointcuts, proxies, and weaving, Spring ensures clean, reusable, and maintainable code. Proper use of AOP improves readability, enforces separation of concerns, and enhances the scalability and robustness of Spring applications.