Clean • Professional
In Spring MVC, HandlerMapping is responsible for routing incoming HTTP requests to the correct controller method. Think of it as a GPS for your requests, determining the exact path each request should take to reach its destination. It acts as a bridge between DispatcherServlet and your controllers, ensuring every request is handled by the right method.
HandlerMapping is a core Spring MVC component that maps a request’s URL, HTTP method, headers, and parameters to a specific controller method. When a request arrives, DispatcherServlet delegates the routing task to HandlerMapping, asking:
“Which controller should handle this request?”
Spring MVC provides multiple HandlerMapping implementations:
@RequestMapping, @GetMapping, @PostMapping, etc. (most commonly used).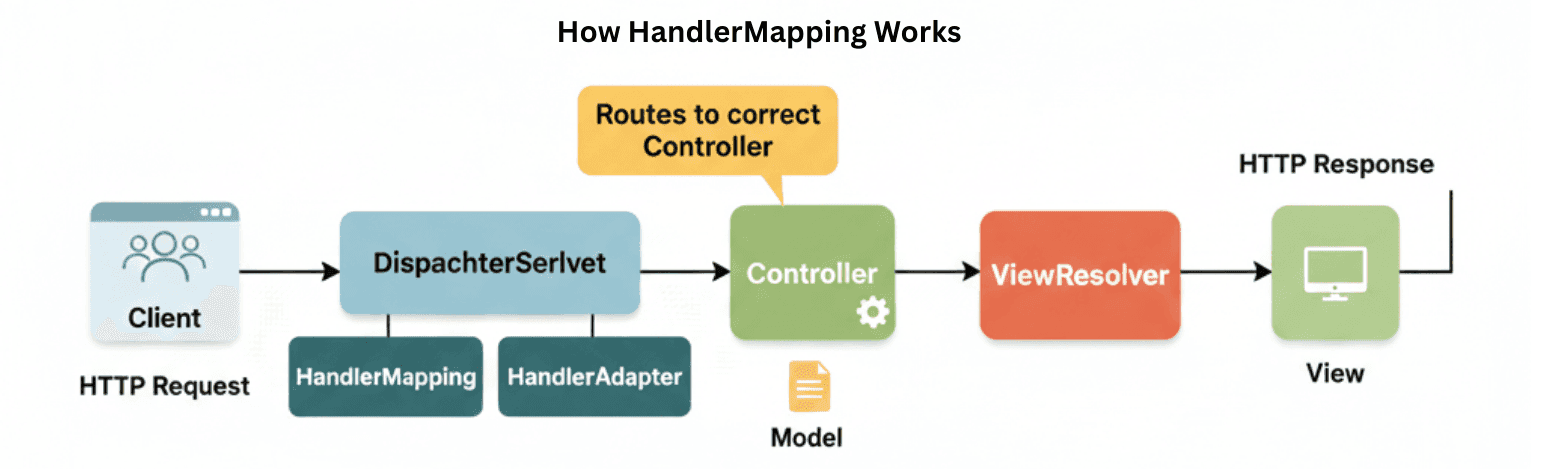
Step-by-Step Flow:
Simplified Flow Diagram:
Client Request → DispatcherServlet → HandlerMapping → Controller → Model → ViewResolver → Response
Spring MVC provides several HandlerMapping implementations to route requests efficiently:
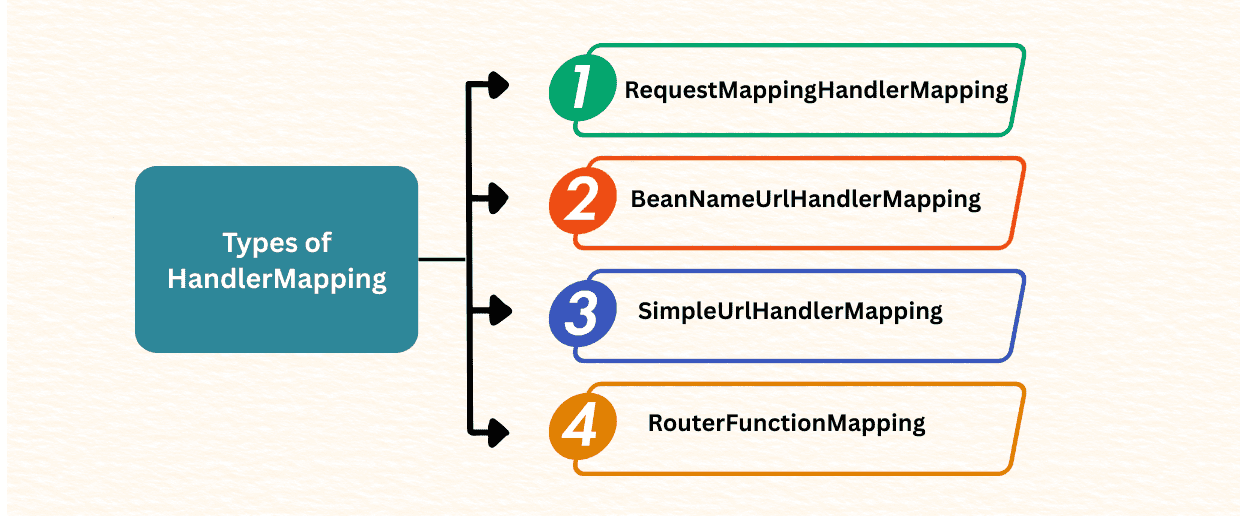
1. RequestMappingHandlerMapping – This is the most commonly used type. It maps requests to methods annotated with @RequestMapping, @GetMapping, @PostMapping, and similar annotations.
Example:
@RestController
publicclassUserController {
@GetMapping("/users")
public List<User>getAllUsers() {
return userService.findAll();
}
}
2. SimpleUrlHandlerMapping – Maps URL paths to controller beans defined in configuration files.
Example (in XML or configuration):
<beanclass="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleUrlHandlerMapping">
<propertyname="mappings">
<props>
<propkey="/home">homeController</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
3. BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping – Maps URL paths directly to controller bean names.
Example:
@Controller("login")
publicclassLoginController {
@RequestMapping("/login")
public StringshowLoginPage() {
return"login";
}
}
4. RouterFunctionMapping – Used in Spring WebFlux for functional routing in reactive applications.
Example:
RouterFunction<ServerResponse> route = RouterFunctions.route(
GET("/users"), request -> ServerResponse.ok().bodyValue(userService.findAll())
);
Among these, RequestMappingHandlerMapping is the most commonly used due to its flexibility and annotation support.
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/users")
publicclassUserController {
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public UsergetUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
return userService.findById(id);
}
@PostMapping
public UsercreateUser(@RequestBody User user) {
return userService.save(user);
}
}
Routing Flow:
GET /users/5 is intercepted by DispatcherServlet.getUser(@PathVariable Long id).HandlerMapping ensures centralized and maintainable routing:
@RequestMapping.HandlerMapping is the routing engine of Spring MVC, directing each incoming request to the right controller method. By working closely with DispatcherServlet and HandlerAdapter, it ensures smooth request handling, clean routing, and a maintainable architecture. Without HandlerMapping, the DispatcherServlet would not know which controller should handle a request, making this component essential for scalable and organized Spring MVC applications.