Clean • Professional
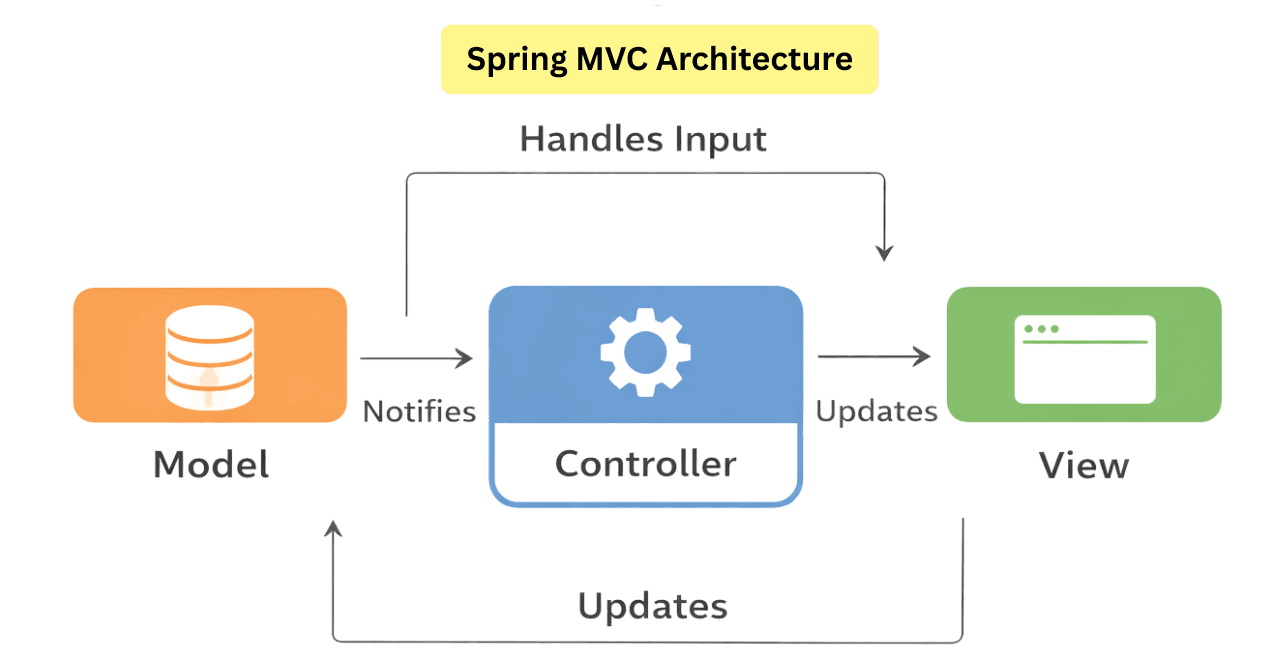
Spring MVC is a powerful framework for building web applications in Java. It follows the Model-View-Controller (MVC) design pattern, which separates an application into three main components: Model, View, and Controller. This separation makes your application scalable, maintainable, and easier to test.
MVC stands for Model-View-Controller, a software design pattern used to organize code into three interconnected layers:
@Controller or @RestController classes.Simplified Flow:
User → Controller → Model → Controller → View → User
Think of it like a restaurant:
Spring MVC is built around several key components that work together to handle web requests, process data, and render responses. Understanding these components is essential for building maintainable and efficient web applications.
Example:
Userhits → <http://localhost:8080/users/1>
The request first goes to DispatcherServlet, not directly to the controller.
Example:
@GetMapping("/users/{id}")
public UsergetUserById(@PathVariable Long id) { ... }
Request:
GET /users/1
➡️ HandlerMapping maps this request to UserController.getUserById()
Example:
@GetMapping("/users/{id}")
public UsergetUserById(@PathVariable Long id) { ... }
HandlerAdapter:
{id} from URLLonggetUserById(1L)Annotations:
@Controller → HTML/JSP views@RestController → REST APIs (JSON/XML)Example (REST API):
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/users")
publicclassUserController {
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public UsergetUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
return userService.findById(id);
}
}
Response:
{
"id":1,
"name":"Rahul"
}
Model, ModelMap, ModelAndView, DTOs.Example:
@GetMapping("/profile")
public StringshowProfile(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("username","Amit");
return"profile";
}
Model contains:
username → Amit
Example:
return"profile";
ViewResolver maps it to:
/WEB-INF/views/profile.jsp
or
profile.html (Thymeleaf)
Example (JSP):
<h1>Welcome, ${username}</h1>
Rendered Output:
Welcome, Amit
Example (REST):
{
"id":1,
"name":"Amit"
}
| Component | Role |
|---|---|
| DispatcherServlet | The front controller; intercepts all HTTP requests and routes them to appropriate handlers. Acts as the main traffic controller. |
| HandlerMapping | Maps user requests (URLs) to the correct controller methods based on path, HTTP method, or metadata. |
| HandlerAdapter | Executes the matched controller method and prepares the response. |
| Controller | Contains methods to handle requests (@Controller or @RestController). Coordinates with the Model. |
| Model | Holds the data to be rendered in the view. Can be DTOs, entities, or simple objects. |
| ViewResolver | Maps logical view names to actual UI templates (e.g., JSP, Thymeleaf, FreeMarker). |
| View | Renders the data from the Model into HTML, JSON, XML, or other formats. |
Diagram Flow (Simplified):
**Client → DispatcherServlet → HandlerMapping → Controller → Service → Repository →
Model → ViewResolver → View → Client**
Spring MVC annotations help in handling requests, passing data, and returning responses in a clean and easy way.
1. @Controller
This annotation marks a class as a Spring MVC controller. It is mainly used in traditional web applications where the response is an HTML or JSP page. The controller method usually returns a view name, which is resolved by a ViewResolver.
@Controller
publicclassHomeController {
@GetMapping("/home")
public Stringhome() {
return"home";
}
}
2. @RestController
This annotation is used to create RESTful web services. Instead of returning a view, it returns data directly in JSON or XML format. It automatically applies @ResponseBody, so there is no need to add it separately.
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/users")
publicclassUserController {
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public UsergetUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
return userService.findById(id);
}
}
3. @RequestMapping
This annotation is used to map HTTP requests to controller classes or methods. It allows you to define the request URL, HTTP method, headers, and parameters. It can be used at both class level and method level.
@RequestMapping(value = "/users", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public List<User>getAllUsers() {
return userService.findAll();
}
4. @GetMapping, @PostMapping, @PutMapping, @DeleteMapping
These annotations are short and cleaner versions of @RequestMapping. Each one is used for a specific HTTP method like GET, POST, PUT, or DELETE, making the code easier to read and understand.
@PostMapping("/users")
public UsercreateUser(@RequestBody User user) {
return userService.save(user);
}
5. @PathVariable
This annotation is used to extract values directly from the URL path. It is commonly used in REST APIs where the resource ID is part of the URL.
@GetMapping("/users/{id}")
public UsergetUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
return userService.findById(id);
}
6. @RequestParam
This annotation is used to read query parameters from the URL. It is often used for pagination, filtering, or optional request values.
@GetMapping("/users")
public List<User>getUsers(
@RequestParamint page,
@RequestParamint size) {
return userService.findAll(page, size);
}
7. @RequestBody
This annotation is used to convert JSON or XML data from the request body into a Java object. It is mainly used with POST and PUT requests.
@PostMapping("/users")
public UsercreateUser(@RequestBody User user) {
return userService.save(user);
}
8. @ResponseBody
This annotation is used to send the method return value directly as JSON or XML instead of returning a view. It is useful when using @Controller but still want to return data.
@GetMapping("/status")
@ResponseBody
public Stringstatus() {
return"Application is running";
}
| Annotation | Description |
|---|---|
@Controller | Marks a class as a Spring MVC controller. Returns a view. |
@RestController | Combination of @Controller + @ResponseBody. Returns JSON/XML directly. |
@RequestMapping | Maps HTTP requests to controller methods. Can specify path, method, headers. |
@GetMapping / @PostMapping / @PutMapping / @DeleteMapping | Shortcuts for specific HTTP methods. |
@PathVariable | Binds URI template variables to method parameters. |
@RequestParam | Binds query parameters to method parameters. |
@RequestBody | Maps request body (JSON/XML) to a Java object. |
@ResponseBody | Converts return value to JSON/XML. |
@Controller
publicclassUserController {
@GetMapping("/user/{id}")
public StringgetUser(@PathVariable Long id, Model model) {
Useruser= userService.getUserById(id);// Fetch data from service layer
model.addAttribute("user", user);// Add data to Model
return"userView";// Logical view name (resolved by ViewResolver)
}
}
Flow:
DispatcherServlet → Controller → Service → Repository → Model → ViewResolver → View → User
@Controller vs @RestController| Feature | @Controller | @RestController |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Marks a class as a Spring MVC controller for views | Marks a class as a controller for REST APIs, returns JSON/XML |
| Response Handling | Returns logical view names (HTML, JSP, Thymeleaf) | Returns objects directly, serialized to JSON/XML automatically |
@ResponseBody | Required on methods returning data | Implicitly applied to all methods (no need for @ResponseBody) |
| Use Case | Server-side rendered web applications | RESTful APIs or microservices |
| Example | java @Controller public class HomeController { @GetMapping("/home") public String home() { return "home"; } } | java @RestController @RequestMapping("/api/users") public class UserController { @GetMapping("/{id}") public User getUser(@PathVariable Long id) { return userService.findById(id); } } |
| View Resolution | Yes, via ViewResolver | No view resolution, data returned directly |
| Serialization | Needs @ResponseBody or ResponseEntity | Automatic serialization (Jackson, JSON/XML) |
| Best For | MVC applications, JSP/HTML pages | REST APIs, JSON services, microservices |
@RestController for APIs and @Controller for web pages.Spring MVC is more than just a framework—it’s a robust architecture for building modern Java web applications. Its clear separation of responsibilities and flexible design make it ideal for production-level apps. By mastering Spring MVC, you can create scalable, maintainable, and SEO-friendly web applications.