Clean • Professional
Testing is a core practice for building reliable, scalable, and production-ready Spring Boot applications. In Spring Boot, repository and service testing ensures that both your data access layer and business logic work correctly, independently, and reliably.
Repository Testing verifies the data access layer. It focuses on checking that JPA repositories, CRUD operations, custom queries, and entity relationships work correctly.
Repository testing ensures:
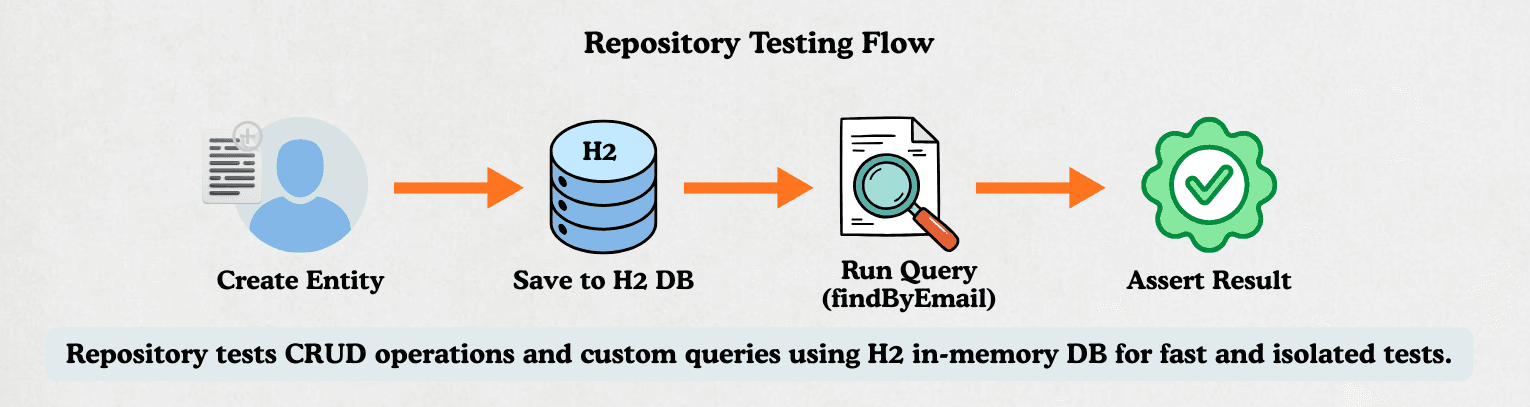
@DataJpaTest@DataJpaTest is designed for repository testing in Spring Boot.
Features of @DataJpaTest:
@DataJpaTest
class UserRepositoryTest {
// Repository tests go here
}
The User entity defines the database table structure with fields like id, name, and email. Entities are used by JPA repositories to perform CRUD operations.
import jakarta.persistence.*;
@Entity
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String name;
private String email;
// Constructors
public User() {}
public User(Long id, String name, String email) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
}
// Getters and Setters
public Long getId() { return id; }
public String getName() { return name; }
public String getEmail() { return email; }
}
The UserRepository interface extends JpaRepository and provides methods to query the database, such as findByEmail. Custom queries can also be added using @Query.
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import java.util.Optional;
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
Optional<User> findByEmail(String email);
}
UserRepositoryTest:The UserRepositoryTest class shows how to test repository methods using @DataJpaTest.
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.DataJpaTest;
import java.util.Optional;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
@DataJpaTest
class UserRepositoryTest {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Test
void shouldFindUserByEmail() {
// Arrange: create and save a new user
User user = new User(null, "Alice", "[email protected]");
userRepository.save(user);
// Act: retrieve the user by email
Optional<User> result = userRepository.findByEmail("[email protected]");
// Assert: verify the user exists and has correct details
assertTrue(result.isPresent());
assertEquals("Alice", result.get().getName());
}
@Test
void shouldReturnEmptyIfUserNotFound() {
// Act: search for a non-existent user
Optional<User> result = userRepository.findByEmail("[email protected]");
// Assert: verify that no user is found
assertFalse(result.isPresent());
}
}
@DataJpaTestRepository testing is fast, reliable, and focuses purely on the database layer.
Service Testing validates the business logic layer.
It ensures that:
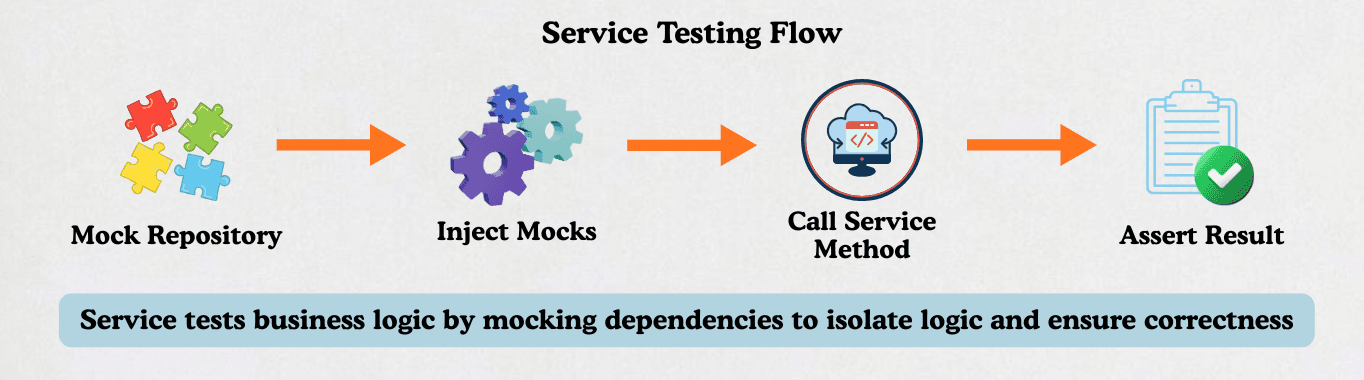
Service testing often mocks dependencies to isolate logic and make tests fast.
@ExtendWith(MockitoExtension.class) – For unit testing services without Spring context@Mock – For mocking repository dependencies@InjectMocks – Inject mocks into the service under test@MockBean – For integration tests with Spring contextUserServiceA simple service interacting with the repository:
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
publicclassUserService {
privatefinal UserRepository userRepository;
publicUserService(UserRepository userRepository) {
this.userRepository = userRepository;
}
// Fetch a user by ID
public UsergetUserById(Long id) {
return userRepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() ->newRuntimeException("User not found"));
}
// Create a new user
public UsercreateUser(User user) {
return userRepository.save(user);
}
}
Key Points:
Unit tests isolate the service logic by mocking dependencies. No database is required, so tests are fast and reliable.
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import org.mockito.InjectMocks;
import org.mockito.Mock;
import org.mockito.Mockito;
import org.mockito.junit.jupiter.MockitoExtension;
import java.util.Optional;
importstatic org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
@ExtendWith(MockitoExtension.class)
classUserServiceTest {
@Mock
private UserRepository userRepository;
@InjectMocks
private UserService userService;
@Test
voidtestGetUserById() {
// Arrange
Useruser=newUser(1L,"Alice","[email protected]");
Mockito.when(userRepository.findById(1L)).thenReturn(Optional.of(user));
// Act
Userresult= userService.getUserById(1L);
// Assert
assertEquals("Alice", result.getName());
}
@Test
voidtestCreateUser() {
// Arrange
Useruser=newUser(null,"Bob","[email protected]");
Mockito.when(userRepository.save(user)).thenReturn(newUser(1L,"Bob","[email protected]"));
// Act
Userresult= userService.createUser(user);
// Assert
assertNotNull(result.getId());
assertEquals("Bob", result.getName());
}
}
Benefits of Mockito for Service Testing:
Sometimes, services need to be tested together with real repositories and database interactions. For this, use @SpringBootTest.
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
importstatic org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
@SpringBootTest
classUserServiceIntegrationTest {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Test
voidtestCreateAndRetrieveUser() {
// Arrange
Useruser=newUser(null,"Charlie","[email protected]");
userService.createUser(user);
// Act
Userretrieved= userService.getUserById(user.getId());
// Assert
assertEquals("Charlie", retrieved.getName());
}
}
| Feature | Repository Testing | Service Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Annotation | @DataJpaTest | Mockito / JUnit / @SpringBootTest |
| Layer Tested | Database & JPA layer | Business logic |
| Dependencies | Real DB (H2 in-memory) | Mocked repositories or services |
| Speed | Fast | Very fast (unit) / Medium (integration) |
| Purpose | CRUD, queries, mappings | Logic, validations, interactions |
@MockBean to isolate dependenciesRepository and service tests help you:
@DataJpaTest@SpringBootTest) combine repository + service testingRepository and service testing are essential for building robust Spring Boot applications. By following these guidelines:
@DataJpaTest for repository tests@ExtendWith for service unit tests@SpringBootTest for full integration testsyou ensure that your data layer works correctly, business rules are enforced, and your application remains bug-free.