Clean • Professional
In Spring MVC, ViewResolver is the component responsible for rendering the final output that users see in their browser. Once the controller finishes processing a request, ViewResolver decides which view file should be used and how that view should be rendered.
In simple terms, the controller decides what data to show, while ViewResolver decides how that data is presented on the screen. This clear separation makes Spring MVC applications clean, flexible, and easy to maintain.
ViewResolver is a core Spring MVC component that maps a logical view name returned by a controller to an actual view technology, such as JSP, Thymeleaf, or FreeMarker.
When a controller returns a view name like:
"home"
"userProfile"
Spring does not know which physical file to render.
The ViewResolver resolves this logical name into a real file path, for example:
/WEB-INF/views/home.jsp
or
templates/userProfile.html
Controllers should focus only on business logic, not on UI rendering details.
Without ViewResolver:
With ViewResolver:
In Spring MVC, every HTTP request follows a well-defined lifecycle. ViewResolver plays its role only when a view needs to be rendered.
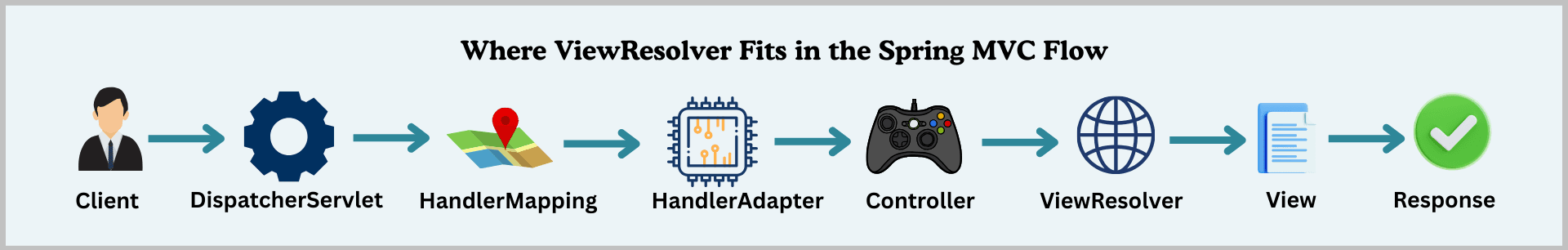
Spring MVC Request Flow
When ViewResolver Is Used
"home" or "userProfile"):
Example:
return"home";
@RestController / @ResponseBodyIn this case:
Example:
return ResponseEntity.ok(user);
When a client sends a request, it flows through the DispatcherServlet and reaches the controller. After processing, the controller returns:
The DispatcherServlet then asks the ViewResolver to resolve the view name.
The ViewResolver:
Simplified Flow
Client → DispatcherServlet → Controller → ViewResolver → View → Response
Controller Code
@Controller
publicclassHomeController {
@GetMapping("/home")
public StringhomePage(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("message","Welcome to Spring MVC");
return"home";
}
}
What Happens Internally
"home" as the logical view name/WEB-INF/views/home.jsp
or
templates/home.html
Spring MVC supports multiple view technologies, each with its own ViewResolver.
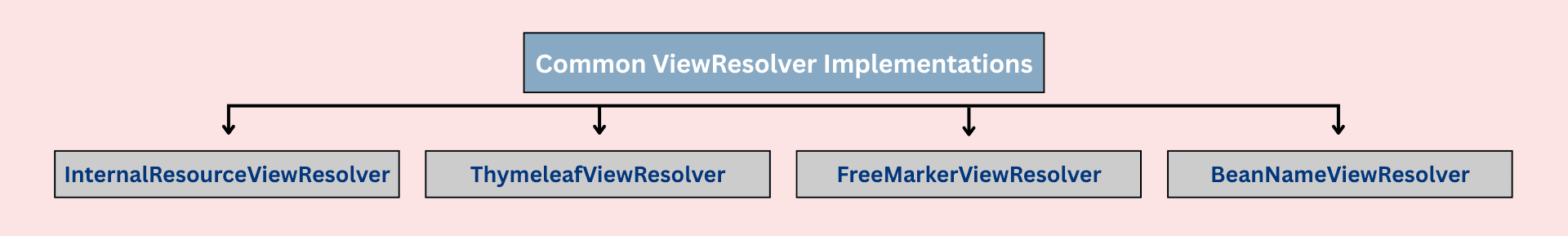
InternalResourceViewResolver
Example:
home → /WEB-INF/views/home.jsp
ThymeleafViewResolver
Used with Thymeleaf templates, especially popular in Spring Boot applications.
Example:
profile → templates/profile.html
FreeMarkerViewResolver
Example:
email → templates/email.ftl
BeanNameViewResolver
ViewResolver provides several key benefits:
| Aspect | ViewResolver (Spring MVC) | REST APIs (Spring MVC / Spring Boot) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Used to render HTML pages that users can directly see in a web browser | Used to return raw data that is consumed by frontend apps, mobile apps, or other services |
| Used In | Traditional server-side web applications such as dashboards, admin panels, and websites | Modern applications like single-page apps, mobile apps, microservices, and integrations |
| Controller Type | Uses @Controller where methods return logical view names | Uses @RestController or @ResponseBody where methods return data directly |
| Return Type | Returns a logical view name such as "home" or "profile" | Returns Java objects like User, List<User>, or ResponseEntity |
| Output | Final response is a fully rendered HTML page | Final response is JSON or XML data |
| View Technology | Works with JSP, Thymeleaf, FreeMarker, or other template engines | Does not use any view technology |
| Rendering Style | Server-side rendering where HTML is generated on the backend | No server-side rendering; only data is sent to the client |
| Uses ViewResolver | Yes, ViewResolver converts logical view names into actual view files | No, ViewResolver is completely skipped |
| Uses HttpMessageConverter | Not used for rendering HTML views | Used to convert Java objects into JSON or XML |
| Client Type | Mainly web browsers where users directly interact with UI | Frontend frameworks, mobile applications, and other backend services |
| Example Endpoint | /home returns an HTML page rendered on the server | /users returns JSON data representing users |
ViewResolver is the rendering engine selector of Spring MVC. After the controller completes its work, ViewResolver takes over to locate the correct view, render it with model data, and send the final response to the client.
Together with DispatcherServlet, HandlerMapping, and HandlerAdapter, ViewResolver completes the Spring MVC request lifecycle, ensuring a clean, flexible, and professional architecture suitable for real-world applications.