Clean • Professional
Enums are one of the most powerful and clean ways to represent fixed sets of constants in Java. They improve readability, remove hard-coded values, and make your code type-safe.
An enum (short for enumeration) is a special data type in Java that defines a fixed set of named constants.
It is used when you know all the possible values at compile time.
Example:
enum Day {
MONDAY, TUESDAY, WEDNESDAY, THURSDAY, FRIDAY, SATURDAY, SUNDAY
}
Enums make your code:
public static final constantsInternally, every enum:
When you write:
enum Color { RED, GREEN }
Internally, Java converts it roughly to:
final class Color extends Enum<Color> {
public static final Color RED = new Color("RED", 0);
public static final Color GREEN = new Color("GREEN", 1);
}
Each constant becomes a public static final object of the enum type.
enum Color {
RED, GREEN, BLUE
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Color c = Color.RED;
System.out.println(c); // Output: RED
}
}
Enums work beautifully with switch-case.
enum Day { MONDAY, FRIDAY, SUNDAY }
switch (Day.FRIDAY) {
case MONDAY:
System.out.println("Start of week");
break;
case FRIDAY:
System.out.println("Weekend is coming!");
break;
case SUNDAY:
System.out.println("Weekend!");
break;
}
Java provides useful methods for all enums:
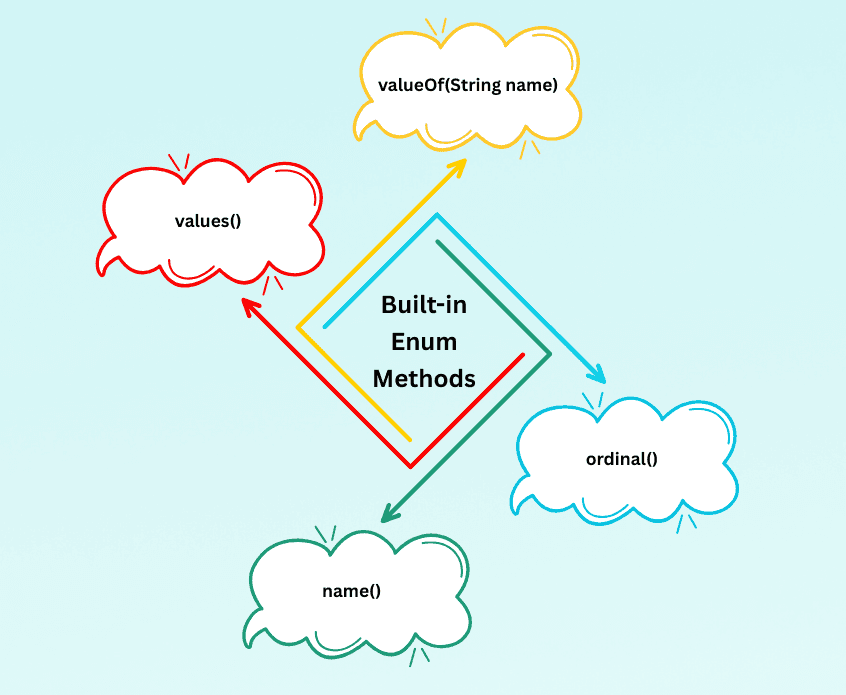
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
values() | Returns all enum constants |
valueOf(String name) | Returns constant with given name |
ordinal() | Returns index (0-based) |
name() | Returns constant name |
for (Day d : Day.values()) {
System.out.println(d + " - Index: " + d.ordinal());
}
Enums can behave like classes.
Example: Enum with Field and Constructor
enum Status {
SUCCESS(200),
ERROR(500),
NOT_FOUND(404);
private int code;
Status(int code) {
this.code = code; // private constructor
}
public int getCode() {
return code;
}
}
Usage:
System.out.println(Status.SUCCESS.getCode()); // Output: 200
enum Level {
LOW {
@Override
public String message() {
return "Low Level";
}
},
HIGH {
@Override
public String message() {
return "High Level";
}
};
public abstract String message();
}
interface Printable {
void print();
}
enum Color implements Printable {
RED, GREEN;
public void print() {
System.out.println("Color: " + this.name());
}
}
Example:
enum OrderStatus {
PENDING, PROCESSING, SHIPPED, DELIVERED, CANCELLED
}