Thread Lifecycle (States of Thread)
A thread in Java goes through several states during its lifecycle. Each state represents what the thread is currently doing. Java officially defines six thread states in the Thread.State enum.
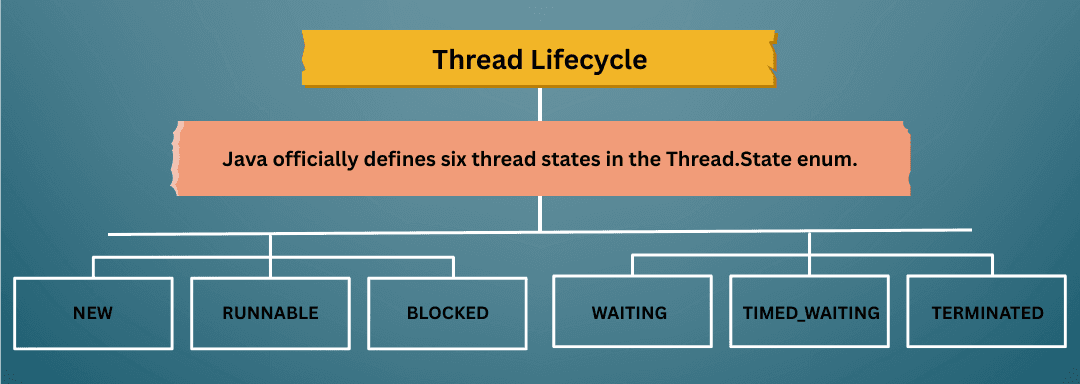
NEW → RUNNABLE → RUNNING → BLOCKED → WAITING → TIMED_WAITING → TERMINATED
Explanation:
1. NEW (Not Started State)
- This is the initial state.
- A thread has been created using the
Threadclass, but itsstart()method has not been called yet. - It exists in memory but has not started executing.
Thread t = new Thread(); // NEW
2. RUNNABLE (Ready-to-Run State)
- After calling start(), the thread enters the RUNNABLE state.
- It is eligible to run but not yet running.
- JVM scheduler will decide when to execute it.
t.start(); // RUNNABLE
3. RUNNING (Actively Executing)
- Thread is actually executing its
run()method. - This is not a separate Java state but part of RUNNABLE in the JVM model.
- Conceptually: RUNNABLE → RUNNING → RUNNABLE.
4. BLOCKED (Waiting for Monitor Lock)
- A thread becomes blocked when it tries to enter a synchronized block or method but another thread already holds the lock.
- It waits until the lock becomes available.
Example:
synchronized(obj) { ... }
5. WAITING (Waiting Indefinitely)
A thread enters the waiting state when it is waiting indefinitely until another thread performs a specific action.
Common causes:
wait()notifyAll()join()without timeoutpark()(LockSupport)
The thread remains here until it is explicitly awakened.
Example:
obj.wait();
6. TIMED_WAITING (Wait for a Fixed Time)
This state occurs when a thread is waiting for a specific time duration.
Common causes:
sleep(1000)wait(500)join(2000)parkNanos()/parkUntil()
After the time expires, the thread becomes runnable again.
Example:
Thread.sleep(1000);
7. TERMINATED (Dead State)
- This is the final state.
- The thread has completed execution of its
run()method or exited due to an exception. - It cannot be restarted.
Simple Lifecycle Diagram
+---------+
| NEW |
+----+----+
|
start()
|
+---------+
| RUNNABLE|
+----+----+
|
scheduler picks
|
+---------+
| RUNNING |
+----+----+
/ | \\
lock missing|wait() \\sleep()
BLOCKED WAITING TIMED_WAITING
\\ | /
+------|--------+
|
task completed
|
+-------------+
| TERMINATED |
+-------------+
How to Check Thread State
Java provides a simple method to check the current state:
System.out.println(thread.getState());

