Clean • Professional
In Java, the final keyword is a non-access modifier that can be applied to variables, methods, and classes.
It is used to restrict modification — once something is declared final, it cannot be changed, overridden, or extended, depending on where it is used.
A final variable means its value cannot be changed after initialization.
It becomes a constant, similar to constants in other programming languages.
Syntax
final dataType variableName = value;
Example – Final Variable
class FinalVariableExample {
final int SPEED_LIMIT = 80;
void display() {
// SPEED_LIMIT = 100; Error: cannot assign a value to final variable
System.out.println("Speed limit: " + SPEED_LIMIT);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new FinalVariableExample().display();
}
}
Output:
Speed limit: 80
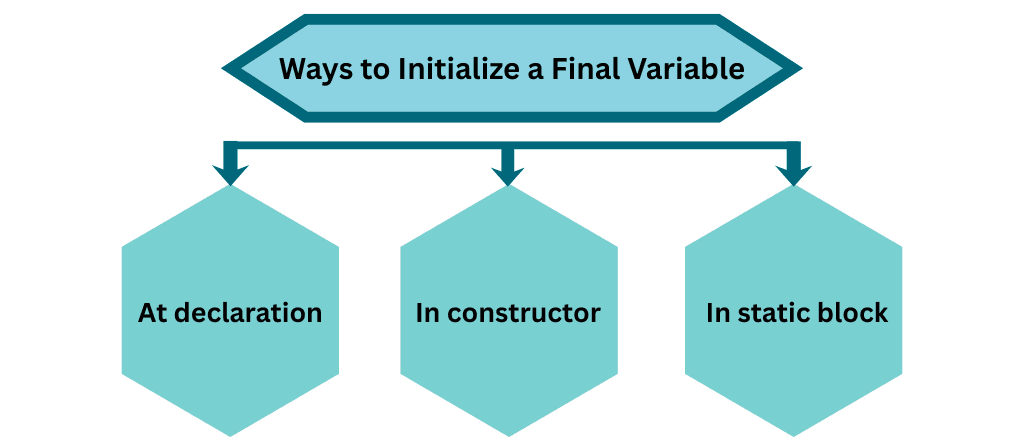
| Type | Example |
|---|---|
| 1. At declaration | final int a = 100; |
| 2. In constructor | Assign in constructor — useful for instance-specific constants |
| 3. In static block | For static final variables |
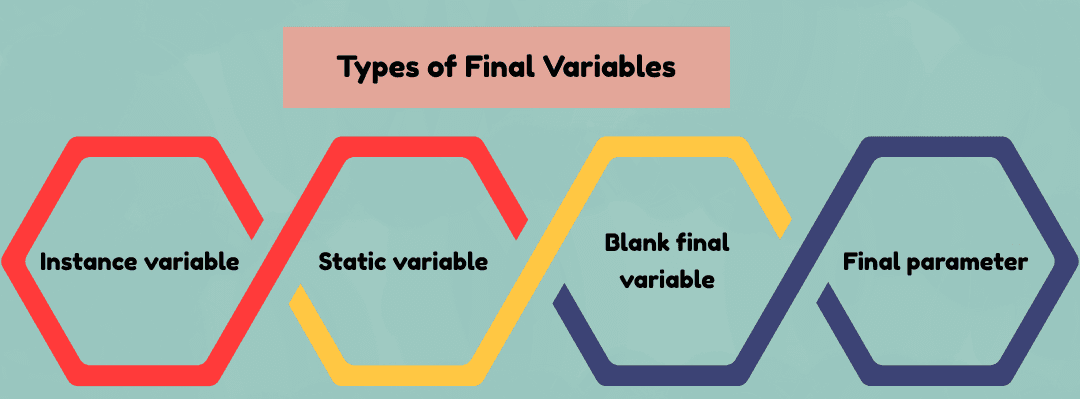
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Instance variable | Belongs to an object | final int x = 10; |
| Static variable | Shared constant for all objects | static final double PI = 3.14159; |
| Blank final variable | Declared but not initialized immediately | Must be initialized in the constructor |
| Final parameter | Method parameter whose value cannot be changed inside the method | void show(final int num) |
Example – Blank Final Variable
class Student {
final int rollNo; // blank final variable
Student(int rollNo) {
this.rollNo = rollNo; // must be initialized in constructor
}
void display() {
System.out.println("Roll No: " + rollNo);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s = new Student(101);
s.display();
}
}
Output:
Roll No: 101
A final method cannot be overridden in a subclass.
This ensures that the method’s behavior remains unchanged for all subclasses.
Syntax
class Parent {
final void show() {
System.out.println("This is a final method.");
}
}
Example – Final Method
class Parent {
final void display() {
System.out.println("Parent method");
}
}
class Child extends Parent {
// void display() { } Error: Cannot override final method
}
public class FinalMethodExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Child c = new Child();
c.display();
}
}
Output:
Parent method
Use Case:
Mark methods as final when you want to prevent subclasses from changing important behavior — like security, logging, or framework methods.
A final class cannot be extended (inherited) by any other class.
This ensures that the class’s structure and behavior cannot be modified through inheritance.
Syntax
final class ClassName {
// class body
}
Example – Final Class
final class Vehicle {
void run() {
System.out.println("Vehicle is running...");
}
}
// class Car extends Vehicle { } Error: cannot inherit from final Vehicle
public class FinalClassExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vehicle v = new Vehicle();
v.run();
}
}
Output:
Vehicle is running...
Use Case:
final classes for security, immutability, or performance reasons.String class in Java is final, so it cannot be extended.When you combine static and final, the variable becomes a constant (a fixed value for the whole class).
Example – Static Final Constant
class Constants {
static final double PI = 3.14159;
static final int MAX_USERS = 100;
}
public class StaticFinalExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("PI = " + Constants.PI);
System.out.println("Max Users = " + Constants.MAX_USERS);
}
}
Output:
PI = 3.14159
Max Users = 100
Commonly used for mathematical constants, configuration values, or fixed limits.
Use of final | Restriction |
|---|---|
| Variable | Value cannot be changed |
| Method | Cannot be overridden |
| Class | Cannot be inherited |
| Use Case | Example |
|---|---|
| Constant values | public static final int MAX_RETRY = 3; |
| Prevent inheritance | final class String { ... } |
| Prevent overriding | final void processPayment() |
| Security and consistency | Prevents changes in critical methods or API classes |
final ≠ finally (exception handling) ≠ finalize() (object cleanup).final objects → their reference cannot change, but their internal data can (if mutable).Example – Final Object Reference
class Demo {
int data = 10;
}
public class FinalObjectExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Demo obj = new Demo();
obj.data = 20; // allowed (object data can change)
// obj = new Demo(); not allowed (reference can't change)
System.out.println(obj.data);
}
}
Output:
20
final is a restriction keyword: no change allowed.final to create constants, secure methods, and non-extendable classes.static final for constants.