Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) in Java
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) is the foundation of Java. It allows developers to write modular, reusable, and maintainable code by focusing on objects rather than procedures.
In Java, almost everything is treated as an object, except primitive types. Understanding OOP is essential for building robust Java applications.
What is OOP in core java?
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) is a method of programming that organizes software design around objects rather than functions or logic.
These objects interact with each other to perform tasks.
Why OOP in Java?
-in-Core-Java_20251108_123454.png&w=3840&q=75)
- Modularity: Break programs into classes and objects.
- Reusability: Use inheritance to reuse existing code.
- Maintainability: Easier to update and debug.
- Security: Encapsulation hides sensitive data.
- Flexibility: Polymorphism allows dynamic method behavior.
Main OOP Principles in Java
There are four key pillars of OOP in Java:
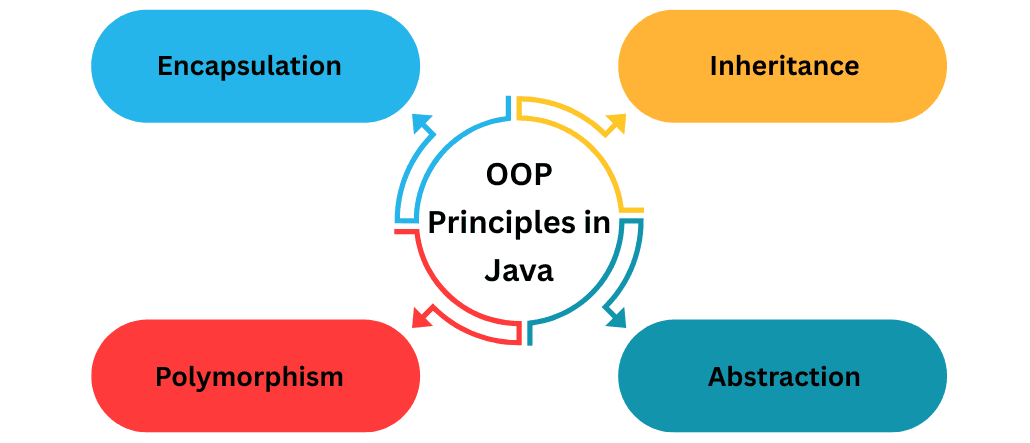
Core Concepts of Java OOP
- Class: Blueprint for creating objects.
- Object: Instance of a class with state (attributes) and behavior (methods).
- Encapsulation: Hiding data using private fields and public getters/setters.
- Inheritance: Allows a class to inherit properties and methods from another.
- Polymorphism: One interface, multiple forms; achieved via method overloading and overriding.
- Abstraction: Hiding implementation details using abstract classes or interfaces.
Example – Simple OOP in Java
class Car {
String color;
int speed;
void drive() {
System.out.println("Car is driving at " + speed + " km/h");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car myCar = new Car();
myCar.color = "Red";
myCar.speed = 80;
myCar.drive();
}
}
Output:
Car is driving at 80 km/h
Notes:
Car→ classmyCar→ object- Encapsulation and methods define state and behavior.
Benefits of OOP in Java
- Reusability of code (through inheritance)
- Maintainability and scalability
- Better organization of complex programs
- Improved data security and modular design
- Easier debugging and modification
Points to Remember
- Java is fundamentally object-oriented.
- OOP enables code reuse, modularity, and better organization.
- Learning OOP is essential before diving into advanced Java concepts like Collections, Multithreading, and JDBC.

