Clean • Professional
Java’s popularity isn’t just because it’s easy to learn — it’s because it’s platform-independent and universally adaptable.
Write Once, Run Anywhere (WORA) means you can write Java code once and run it on Windows, Linux, macOS, or Android — without changing a single line.
This unique capability, powered by Bytecode and the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), is one of the main reasons why Java dominates the software industry even after 25+ years.
Platform independence means that a Java program written on one operating system can run on any other OS that has a Java Virtual Machine (JVM) installed.
In other words —
Write once, run anywhere.
This is the core philosophy that made Java famous.
The secret lies in Bytecode — an intermediate form of your Java code.
Here’s the process
Hello.javajavac) converts it into bytecode – Hello.classThis means you don’t need separate versions of your program for each operating system.
Bytecode is a special, platform-neutral code generated after compilation of a Java program.
It’s stored in .class files and can be executed by any JVM.
Think of it like this:
Java Compiler → creates Bytecode
JVM → translates Bytecode → Machine CodeExample
class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello Java!");
}
}When compiled
javac HelloWorld.javait generates
HelloWorld.classNow you can run:
java HelloWorld
Output:
Hello Java!
That’s the magic of platform independence!
Source Code (.java)
↓
Java Compiler (javac)
↓
Bytecode (.class)
↓
Java Virtual Machine (JVM)
↓
Native Machine Code
↓
Output (Runs Anywhere!)
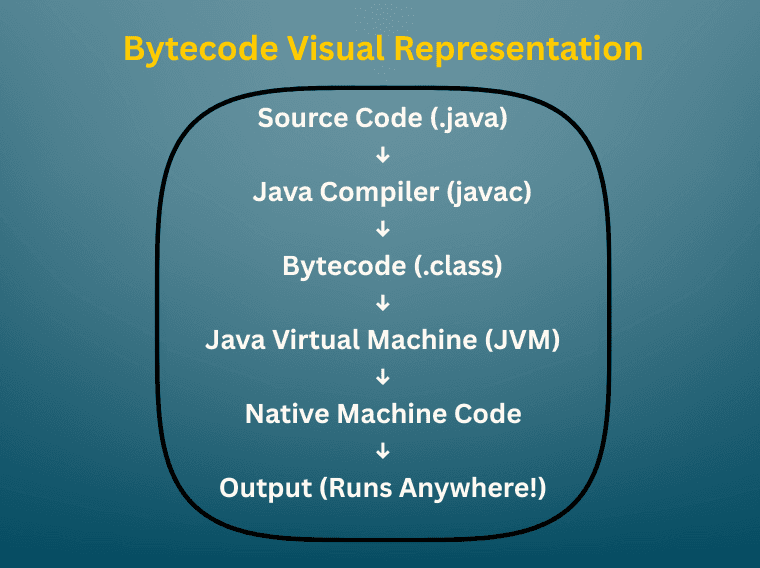
Each platform has its own JVM implementation, but bytecode stays the same everywhere — that’s why Java is portable.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Portability | Same program runs on any OS with JVM |
| Cost-Effective | No need to rewrite or recompile for each platform |
| Consistency | Uniform behavior across all systems |
| Scalability | Easy to deploy on multiple platforms |
| Future-Ready | Supports cross-platform enterprise solutions |
Now that you understand how Java runs anywhere, let’s explore where it’s used.
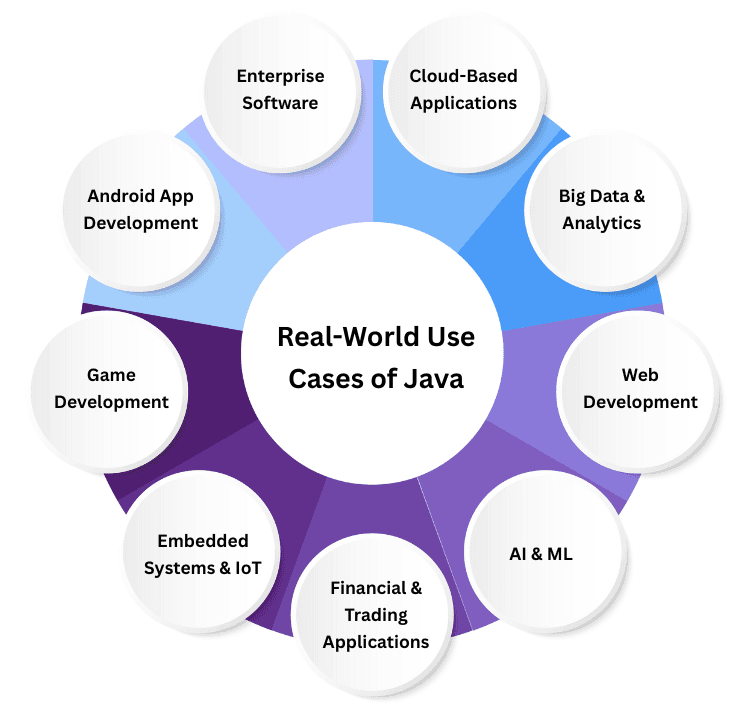
Example: REST APIs and distributed cloud apps.
Example: Data processing & ML workflows.