Clean • Professional
Immutable collections are collections that cannot be modified after creation. Once you create them, you cannot add, remove, or change elements.
Java 9 introduced new convenient factory methods to create immutable List, Set, and Map objects easily and safely.
An immutable collection is a collection whose elements cannot be added, removed, or updated once it is created.
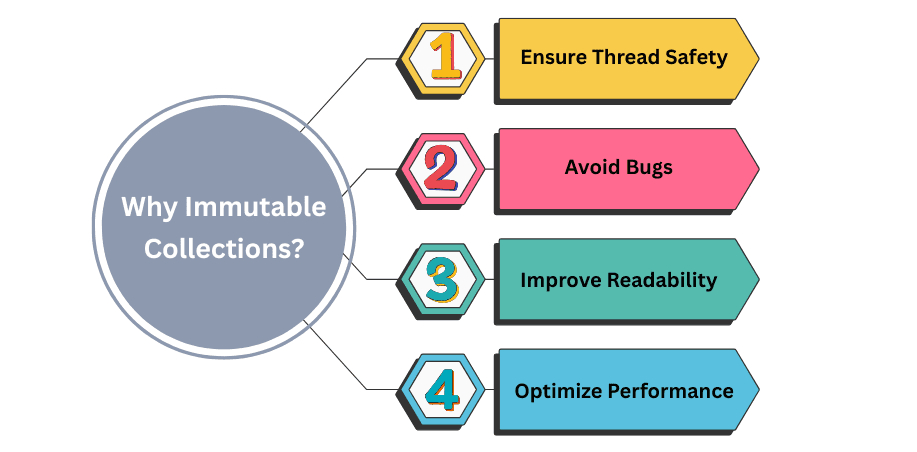
Immutable collections are useful because they:
Java 9 introduced factory methods in List, Set, and Map interfaces to create immutable collections:
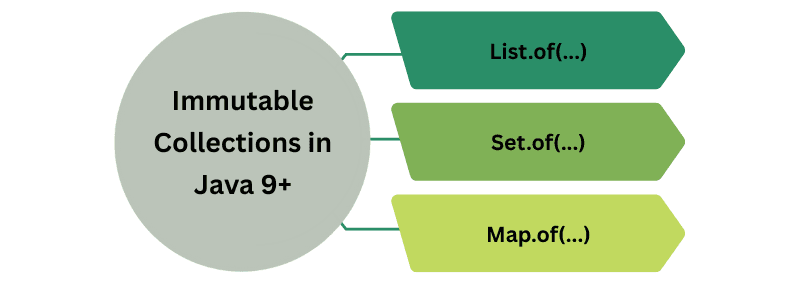
List.of(...)Set.of(...)Map.of(...)1. Immutable List
import java.util.List;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = List.of("A", "B", "C");
System.out.println(list); // [A, B, C]
// list.add("D"); // Throws UnsupportedOperationException
// list.remove("A"); // Throws UnsupportedOperationException
}
}
Key Points:
null elements (throws NullPointerException)2. Immutable Set
import java.util.Set;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<String> set = Set.of("X", "Y", "Z");
System.out.println(set); // [X, Y, Z]
// set.add("A"); // UnsupportedOperationException
}
}
Key Points:
null3. Immutable Map
import java.util.Map;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Integer, String> map = Map.of(1, "One", 2, "Two", 3, "Three");
System.out.println(map); // {1=One, 2=Two, 3=Three}
// map.put(4, "Four"); // UnsupportedOperationException
}
}
Key Points:
null keys or values are not allowedFor more than 10 entries, use:
Map<Integer, String> map = Map.ofEntries(
Map.entry(1, "One"),
Map.entry(2, "Two"),
Map.entry(3, "Three")
);
For maps with more than 10 entries, use Map.ofEntries():
Map<String, Integer> scores = Map.ofEntries(
Map.entry("Alice", 90),
Map.entry("Bob", 85),
Map.entry("Charlie", 92)
);
| Feature | Java 8 | Java 9+ |
|---|---|---|
| Creation | Collections.unmodifiableList(...) | List.of(...) |
| Nulls | Allows nulls | NullPointerException for null elements |
| Conciseness | Verbose | Concise & readable |
| Performance | Extra wrapper object | Optimized built-in immutable objects |
Collections.unmodifiable*() vs List.of()List<String> fruits = new ArrayList<>();
fruits.add("Apple");
fruits.add("Banana");
List<String> unmodifiableFruits = Collections.unmodifiableList(fruits);
List<String> fruits = List.of("Apple", "Banana");
// Truly immutable and concise
List.of, Set.of, Map.of) instead of Collections.unmodifiableListImmutable Collections (Java 9+):
List.of, Set.of, Map.of