Clean • Professional
Both EnumSet and EnumMap are special Collection classes designed exclusively for enum types.
They are extremely fast, lightweight, memory-efficient, and perform better than traditional Set/Map implementations when working with enums.
Both belong to the java.util package.
EnumSet is a specialized Set implementation created only for enum types. It stores enum constants using a bit-vector representation, making it extremely fast and memory-efficient.

NullPointerException.HashSet for add, remove, and contains.| Method | Description |
|---|---|
EnumSet.of() | Create a set with selected enum constants |
EnumSet.allOf() | Includes all enum constants |
EnumSet.noneOf() | Creates an empty EnumSet of given enum type |
EnumSet.range(e1, e2) | Includes values from e1 → e2 |
EnumSet.complementOf() | Returns all enums not in the given set |
add() / remove() | Add or remove an element |
contains() | Check if element exists |
1. Creating an EnumSet
enum Day { MON, TUE, WED, THU, FRI, SAT, SUN }
EnumSet<Day> weekdays = EnumSet.of(Day.MON, Day.TUE, Day.WED, Day.THU, Day.FRI);
2. Selecting All Values
EnumSet<Day> allDays = EnumSet.allOf(Day.class);
3. Range Example
EnumSet<Day> midWeek = EnumSet.range(Day.TUE, Day.THU);
4. Complement Example
EnumSet<Day> weekend = EnumSet.complementOf(weekdays);
Use EnumSet when:
Common Use Cases:
allOf, range, complementOf)Collections.synchronizedSet() if needed)EnumMap is a specialized Map implementation where keys must be enum constants.
It is backed internally by a simple array, making it faster and lighter than HashMap whenever the keys are enums.
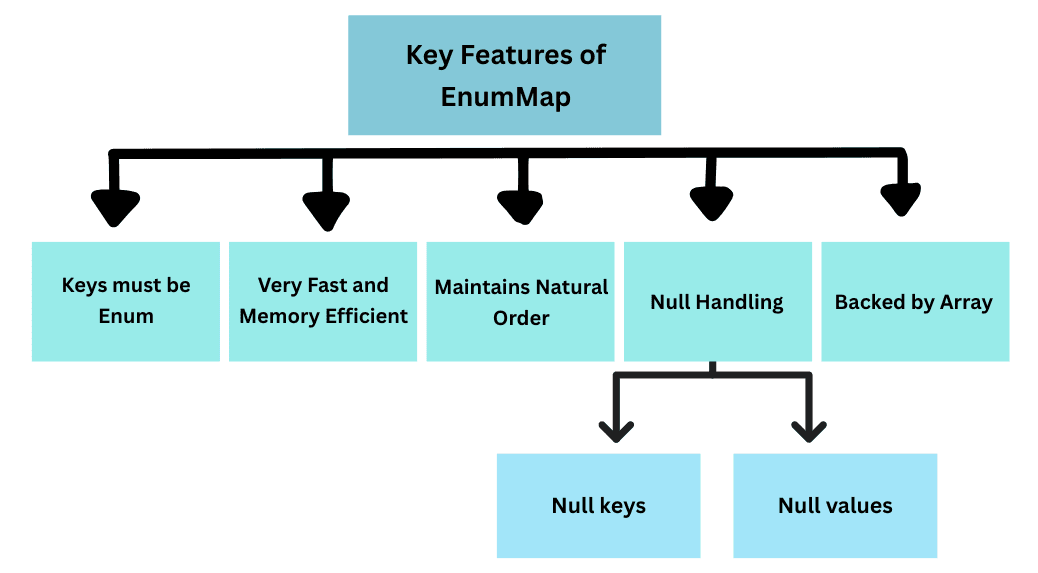
HashMap when keys are enum constants.NullPointerException| Method | Description |
|---|---|
put(key, value) | Adds a key–value pair |
get(key) | Gets the value |
containsKey(key) | Checks if key exists |
remove(key) | Removes an entry |
entrySet() | Returns all entries |
size() | Returns total number of entries |
Enum Declaration
enum Status { NEW, IN_PROGRESS, COMPLETED }
EnumMap Usage
EnumMap<Status, String> map = new EnumMap<>(Status.class);
map.put(Status.NEW, "Task Created");
map.put(Status.IN_PROGRESS, "Task Running");
map.put(Status.COMPLETED, "Task Done");
System.out.println(map);
Output
{NEW=Task Created, IN_PROGRESS=Task Running, COMPLETED=Task Done}
Use EnumMap when:
Common Use Cases:
Collections.synchronizedMap() if required)| Feature | EnumSet | EnumMap |
|---|---|---|
| Stores | Only enum values | Key = Enum, Value = Any type |
| Internal structure | Bit-vector | Array-based |
| Order | Natural order of enums | Natural order of enum keys |
| Performance | Very fast | Fast |
| Use-case | Representing group of enum constants | Mapping enum → value |