Clean • Professional
The Java Collections Framework (JCF) is a unified architecture that provides interfaces, classes, and algorithms for storing and manipulating groups of objects. It simplifies working with data structures and allows developers to choose the right collection type based on their requirements.
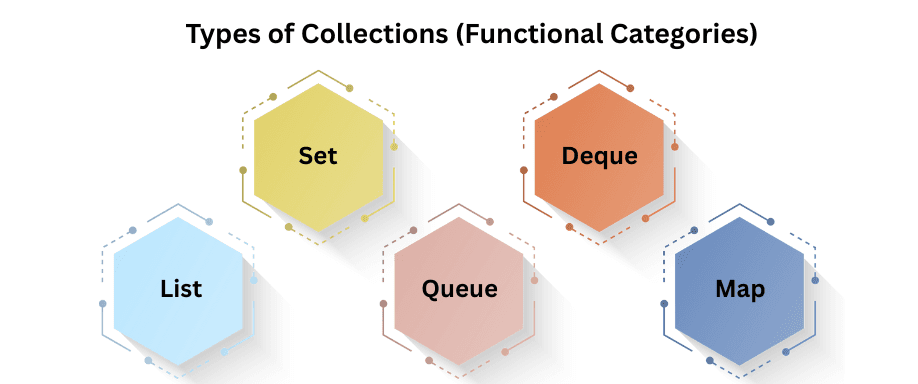
Collections can store data in lists, sets, queues, or maps, each with distinct behavior.
These are interfaces defined in the Collections Framework. They define behavior/contract that collection classes implement. Some are subinterfaces.
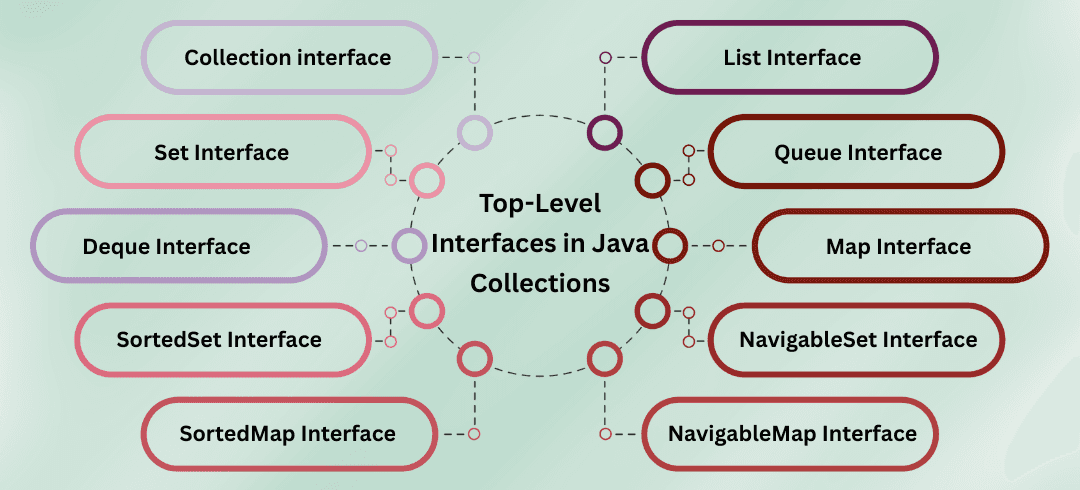
Iterable (Root interface)
│
Collection (Parent)
┌─────────────┬─────────────┬─────────────┐
│ │ │
List Set Queue
│ │ │
┌───────┴───────┐ │ ┌───────┴───────┐
│ │ │ │ │
ArrayList LinkedList HashSet LinkedHashSet PriorityQueue
Vector Stack TreeSet NavigableSet ArrayDeque
Map (Separate)
├──────────────┬─────────────┬──────────────┐
HashMap LinkedHashMap TreeMap (SortedMap) NavigableMap
iterator() method to traverse elements.for-each loops.Iterable
└── Collection
Iterable.add(), remove(), size(), contains(), iterator().Example:
Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<>();
coll.add("Apple");
coll.add("Banana");
System.out.println(coll.contains("Apple")); // true
Note: Map is not part of the Collection hierarchy.
Common Implementations: ArrayList, LinkedList, Vector, Stack.
Example:
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("A");
list.add("B");
list.add("A"); // duplicates allowed
System.out.println(list); // [A, B, A]
Common Implementations: HashSet, LinkedHashSet, TreeSet.
Example:
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add("A");
set.add("B");
set.add("A"); // duplicate ignored
System.out.println(set); // [A, B] (unordered)
Common Implementations: PriorityQueue, LinkedList, ArrayDeque.
Example:
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(10);
queue.add(20);
System.out.println(queue.poll()); // 10 (FIFO)
Common Implementations: ArrayDeque, LinkedList.
Deque (Double-Ended Queue)
Queue ──> Deque
├── ArrayDeque
└── LinkedList
Example:
Deque<String> deque = new ArrayDeque<>();
deque.addFirst("A");
deque.addLast("B");
System.out.println(deque); // [A, B]
Collection, but a top-level interface.Common Implementations: HashMap, LinkedHashMap, TreeMap, NavigableMap.
Map Hierarchy (Separate Branch)
Map
├── HashMap
├── LinkedHashMap
├── TreeMap (SortedMap)
│ └── NavigableMap
└── Hashtable (Legacy)
Example:
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("A", 100);
map.put("B", 200);
System.out.println(map.get("A")); // 100
ceiling(), floor(), higher(), lower().SortedSet & NavigableSet
Set (Specialized)
└── SortedSet
└── NavigableSet
Example:
NavigableSet<Integer> navSet = new TreeSet<>();
navSet.add(10);
navSet.add(20);
System.out.println(navSet.ceiling(15)); // 20
ceilingKey(), floorKey(), higherKey(), lowerKey().SortedMap & NavigableMap
Map (Specialized)
└── SortedMap
└── NavigableMap
Example:
NavigableMap<Integer, String> navMap = new TreeMap<>();
navMap.put(1, "A");
navMap.put(3, "C");
System.out.println(navMap.higherKey(1)); // 3
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| List | Ordered collection, duplicates allowed, index-based |
| Set | Unique elements, unordered/sorted, no index |
| Queue | FIFO or priority-based collection |
| Deque | Double-ended queue, supports both ends |
| Map | Key-value pairs, keys unique, values may duplicate |
Subinterfaces like SortedSet, NavigableSet, SortedMap, and NavigableMap are specialized versions of Set or Map.
Start
│
▼
Iterable (Root)
│
▼
Collection
│
├───────────────┬───────────────┬───────────────┐
▼ ▼ ▼ ▼
List Set Queue Map
│ │ │ │
▼ ▼ ▼ ▼
ArrayList HashSet PriorityQueue HashMap
LinkedList LinkedHashSet LinkedList LinkedHashMap
Vector TreeSet ArrayDeque TreeMap (SortedMap)
Stack SortedSet Deque NavigableMap
NavigableSet
iterator() or for-each loops.