Clean • Professional
A PriorityQueue in Java is a special type of queue where elements are ordered based on priority, not insertion order.
It is part of the java.util package and implements the Queue interface.
A PriorityQueue arranges elements in natural ordering (ascending order for numbers, alphabetical for strings) unless a custom Comparator is given.
Example:
If you insert → 30, 10, 20
PriorityQueue stores → 10, 30, 20 (internally, heap structure)
Iterable
└── Collection
└── Queue
└── PriorityQueue
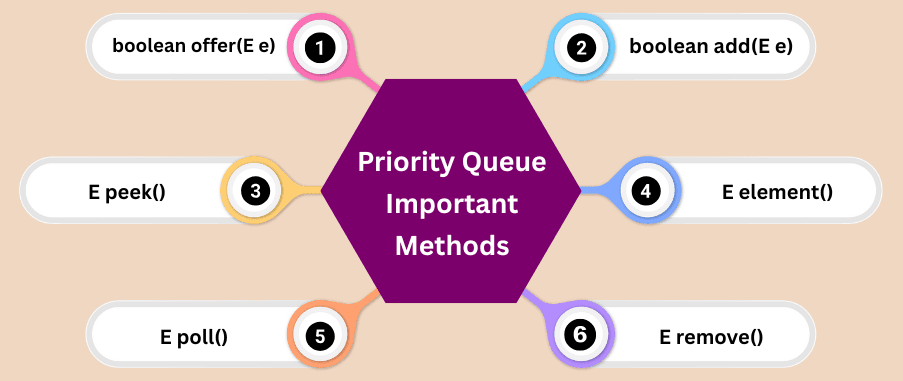
boolean offer(E e)
Adds an element to the queue. Returns true on success.
boolean add(E e)
Adds an element. Throws exception if it fails.
E peek()
E element()
Same as peek() but throws an exception when empty.
E poll()
E remove()
PriorityQueue Example
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.offer(30);
pq.offer(10);
pq.offer(20);
System.out.println(pq.poll()); // 10
System.out.println(pq.poll()); // 20
System.out.println(pq.poll()); // 30
}
}
10
20
30
Even though inserted as 30, 10, 20 → output is sorted by priority.
PriorityQueue<String> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.offer("Banana");
pq.offer("Apple");
pq.offer("Cherry");
System.out.println(pq.poll()); // Apple
Use Comparator:
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq =
new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.reverseOrder());
pq.offer(30);
pq.offer(10);
pq.offer(20);
System.out.println(pq.poll()); // 30
class Student {
String name;
int marks;
Student(String name, int marks) {
this.name = name;
this.marks = marks;
}
}
PriorityQueue<Student> pq =
new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> b.marks - a.marks); // High marks = high priority
pq.offer(new Student("Ram", 85));
pq.offer(new Student("Shyam", 92));
pq.offer(new Student("Mohan", 78));
System.out.println(pq.poll().name); // Shyam
Use PriorityQueue for:
| Feature | Queue | PriorityQueue |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A linear data structure that follows FIFO (First-In First-Out). | A special type of Queue where elements are removed based on priority, not order. |
| Ordering Rule | Maintains insertion order. | Maintains priority order (natural or custom comparator). |
| Removal Type | Removes the first inserted element. | Removes the highest-priority element. |
| Internal Working | Usually backed by LinkedList or ArrayDeque. | Internally implemented using a Binary Heap. |
| Null Elements | Allowed only in some implementations (LinkedList , ArrayDeque ). | Not allowed (throws NullPointerException). |
| Performance (Insertion/Removal) | O(1) in most implementations. | O(log n) because heap needs reordering. |
| Custom Sorting | Not supported. | Supported using Comparator. |
| Use Case | Simple FIFO operations (queueing tasks, buffering). | Priority-based tasks (task scheduling, algorithms like Dijkstra, Huffman). |
| Ordering Guarantee | Predictable, ordered. | No guarantee of insertion order. |
| Examples | LinkedList, ArrayDeque, PriorityQueue (as Queue), etc. | PriorityQueue (only one implementation). |