Clean • Professional
Thread Pools in Java let you run multiple tasks efficiently without creating a new thread for each task. Creating threads frequently can slow down your program and use too much memory.
A Thread Pool is a collection of pre-created, reusable threads that can execute tasks. Instead of creating new threads every time, Java reuses existing threads to handle tasks quickly and efficiently.
The ExecutorService in Java is the most common way to create and manage thread pools.
Thread Pools improve performance, save memory, and make multithreaded programming easier.
A Thread Pool is like a team of workers ready to pick up tasks from a queue. Instead of hiring a new worker for every job, the team handles tasks efficiently.
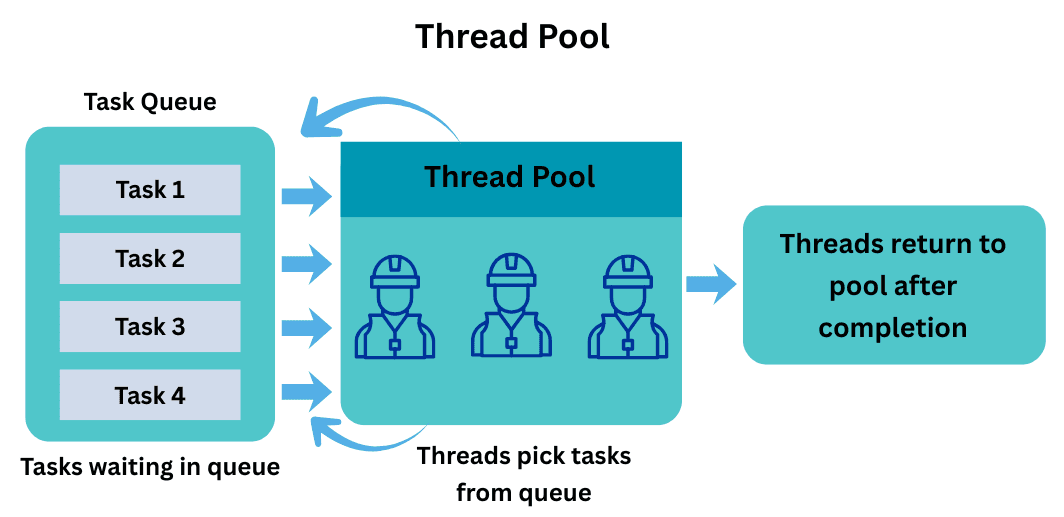
Why use a Thread Pool?
Runnable or Callable).This ensures efficient resource use and faster task execution.
Java’s Executor framework provides several ready-to-use thread pool types via the Executors class:
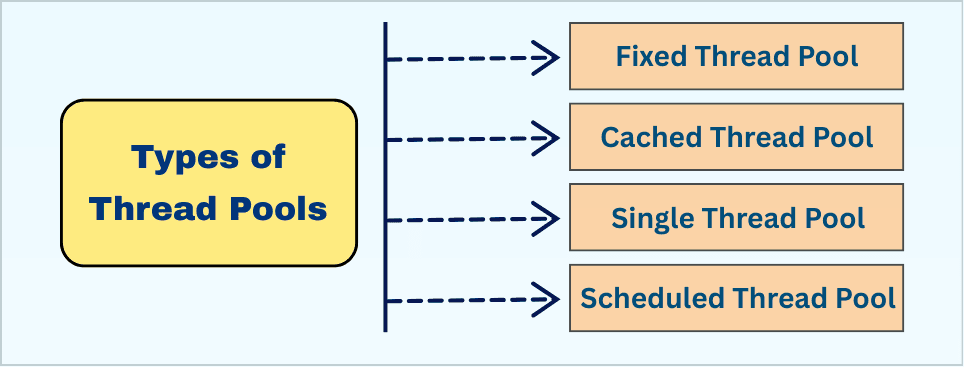
1. Fixed Thread Pool:
ExecutorServiceexecutor= Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
2. Cached Thread Pool:
ExecutorServiceexecutor= Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
3. Single Thread Pool:
ExecutorServiceexecutor= Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
4. Scheduled Thread Pool:
ScheduledExecutorServiceexecutor= Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2);
Advanced Control: Use ThreadPoolExecutor to customize:
corePoolSizemaximumPoolSizekeepAliveTimeBlockingQueue typeHere’s a simple example using a fixed thread pool:
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
publicclassThreadPoolExample {
publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args) {
// Create a pool with 3 threads
ExecutorServiceexecutor= Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
// Submit 5 tasks to the pool
for (inti=1; i <=5; i++) {
inttaskNumber= i;
executor.submit(() -> {
System.out.println("Executing Task " + taskNumber +" by " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);// Simulate work
}catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
// Shutdown the executor
executor.shutdown();
}
}
Explanation:
newFixedThreadPool(3) → Creates a pool with 3 threads.submit() → Adds tasks to the pool.shutdown() → Stops accepting new tasks and shuts down threads after finishing current tasks.Thread Pools are essential in Java programming. They improve performance, save memory, and simplify multithreading. Using the right thread pool, especially with ExecutorService, ensures your program runs fast, efficiently, and reliably.
Learning Thread Pools is crucial for developers building scalable and high-performance Java applications.